Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2020; 26(28): 4094-4107
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4094
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4094
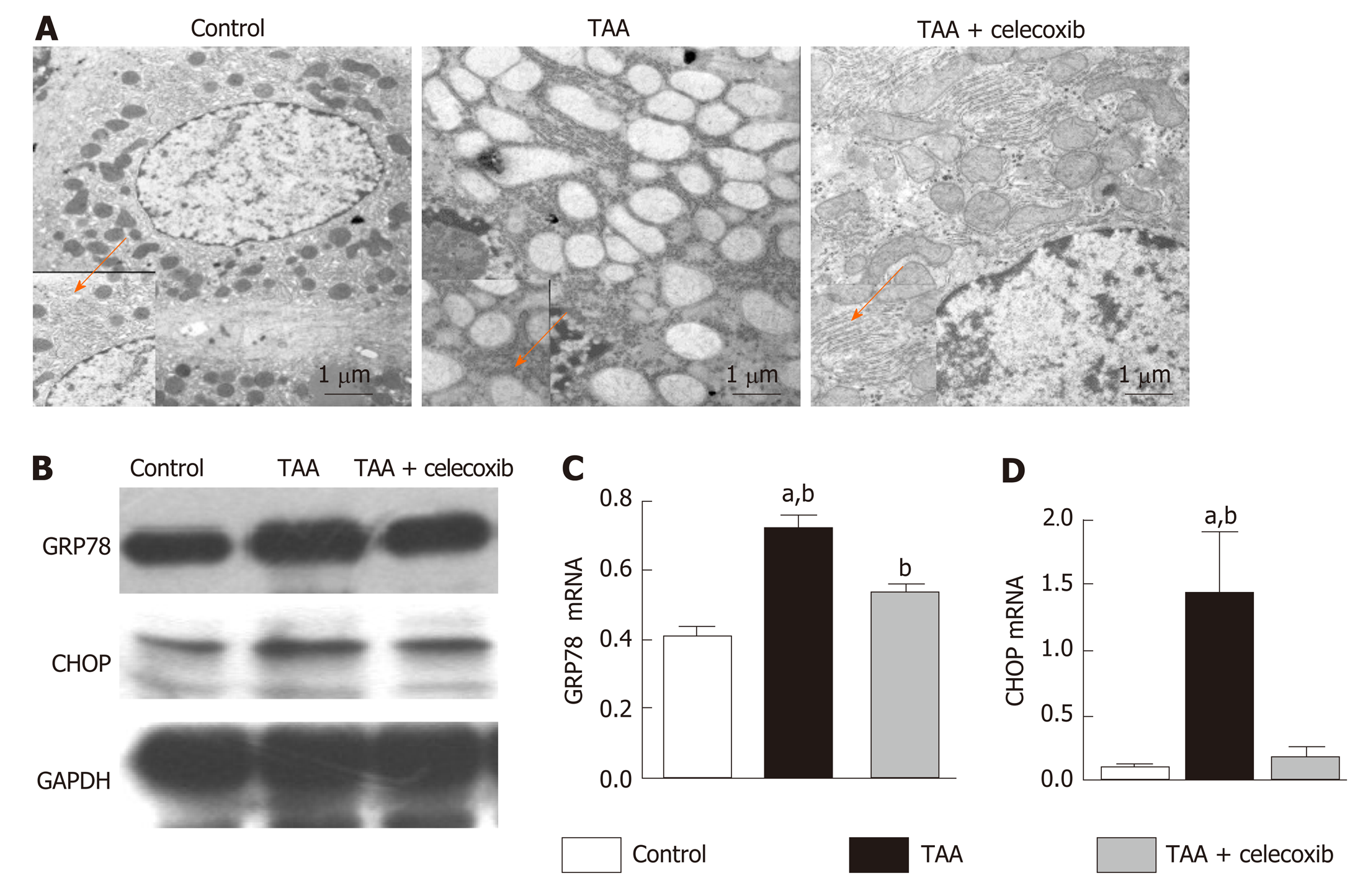
Figure 3 Celecoxib inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress.
A: Hepatocytes in the thioacetamide (TAA) and TAA + celecoxib groups (transmission electron microscopy, × 6000-10000); B: Hepatic glucose-regulated protein 78 and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein expression measured by Western blot. n = 6/group; C and D: Quantitative Western blot results. aP < 0.05 vs TAA + celecoxib group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; CHOP: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein. TAA: Thioacetamide.
- Citation: Su W, Tai Y, Tang SH, Ye YT, Zhao C, Gao JH, Tuo BG, Tang CW. Celecoxib attenuates hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(28): 4094-4107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i28/4094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4094