Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2020; 26(28): 4055-4075
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4055
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4055
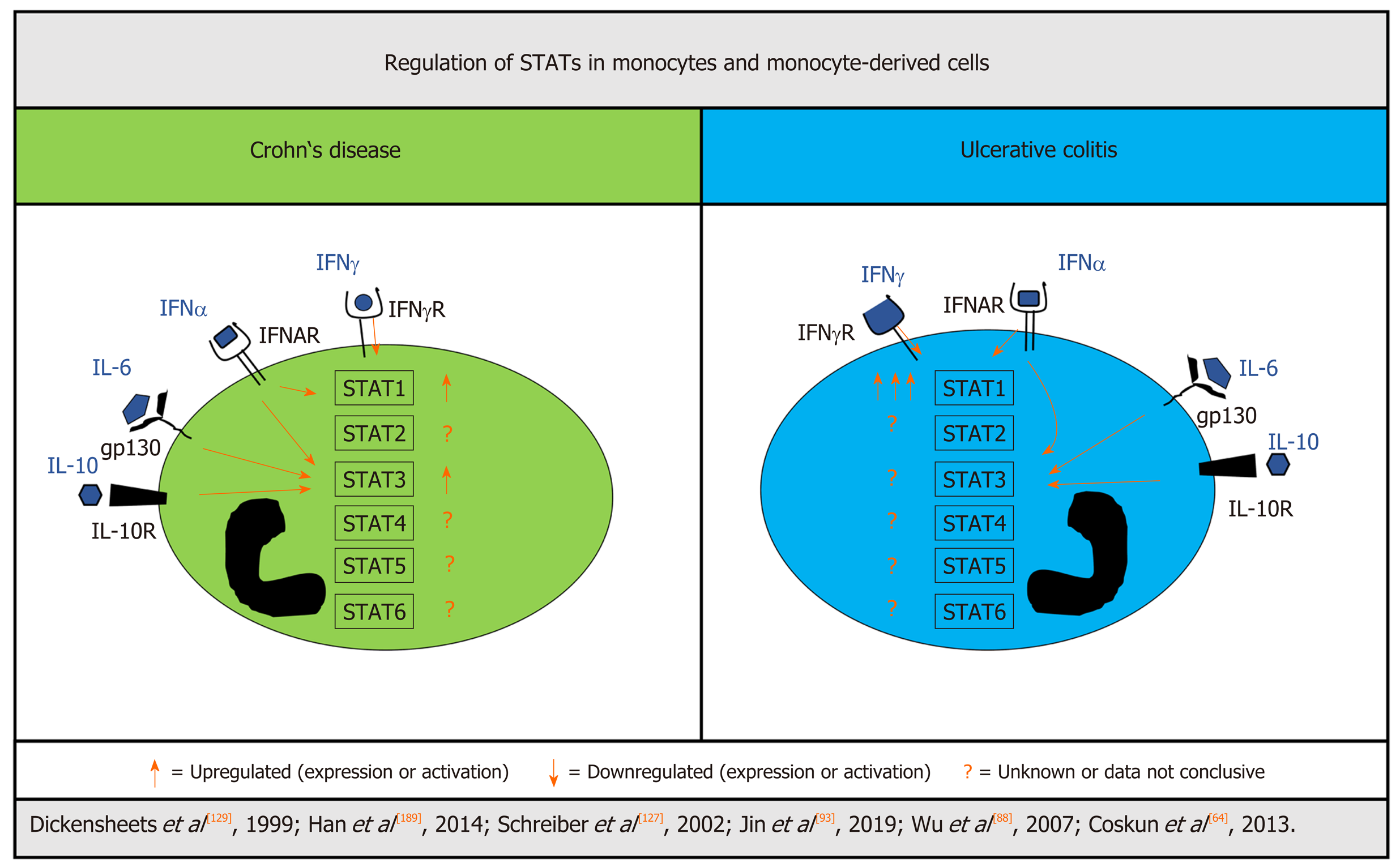
Figure 3 Differentially regulated STATs in monocytes and monocyte-derived cells from patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 activation seems to be different in myeloid cells of patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Although induced in CD, STAT1 is greatly elevated in monocytes and monocyte-derived cells from UC. There is evidence for increased STAT3 signaling in CD, while UC was not investigated. For STAT2, STAT4, STAT5, and STAT6 there are no solid data available from patients with IBD. Count of arrows indicates strength of increase in a direct comparison of UC and CD. CD: Crohn’s disease; IFN: Interferon; IFNAR: Interferon α receptor; IFNγ-R: Interferon γ receptor; IL: Interleukin; IL10R: Interleukin 10 receptor; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Cordes F, Foell D, Ding JN, Varga G, Bettenworth D. Differential regulation of JAK/STAT-signaling in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(28): 4055-4075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i28/4055.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4055