Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2020; 26(28): 4055-4075
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4055
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4055
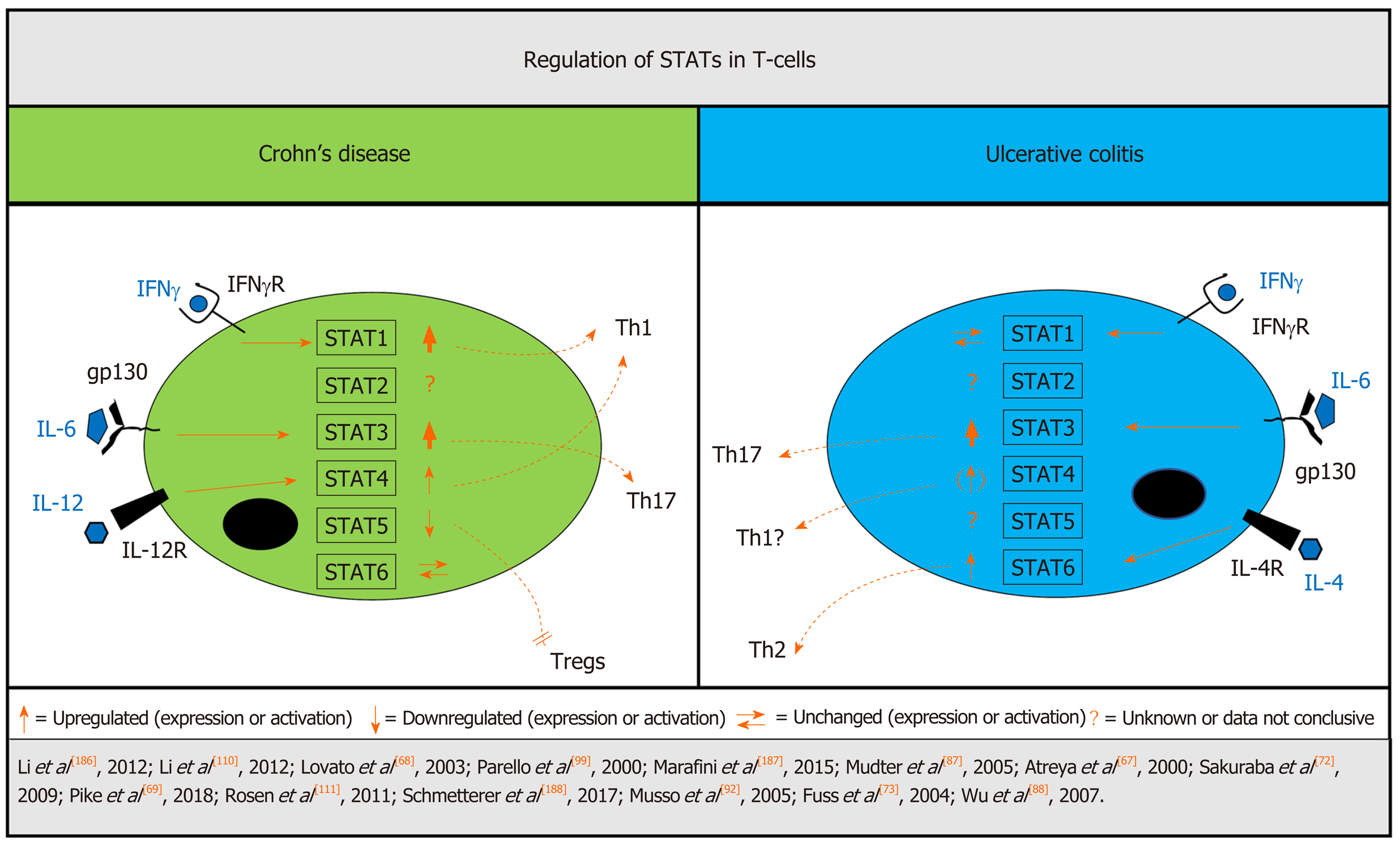
Figure 2 Differentially regulated STATs in T-cells from patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
In T-cells, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 signaling is increased in Crohn`s disease (CD) but not ulcerative colitis (UC), while STAT3 is associated with a critical role in both UC and CD pathogenesis and overactivation is linked to increased intestinal inflammation. There is stronger evidence of STAT4 signaling in CD but STAT4 induction is also apparent in UC, while the STAT6 pathway seems to be more affected in UC. Down-regulation of STAT5 in CD leads to inhibition of regulatory T-cells. Strength of arrows indicates available supporting data. CD: Crohn’s disease; IFN: Interferon; IFNγ-R: Interferon γ receptor; IL: Interleukin; IL4R: Interleukin 4 receptor; IL12R: Interleukin 12 receptor; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; Th: T-helper cell; Treg: Regulatory T-cell; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Cordes F, Foell D, Ding JN, Varga G, Bettenworth D. Differential regulation of JAK/STAT-signaling in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(28): 4055-4075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i28/4055.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4055