Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2020; 26(26): 3750-3766
Published online Jul 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i26.3750
Published online Jul 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i26.3750
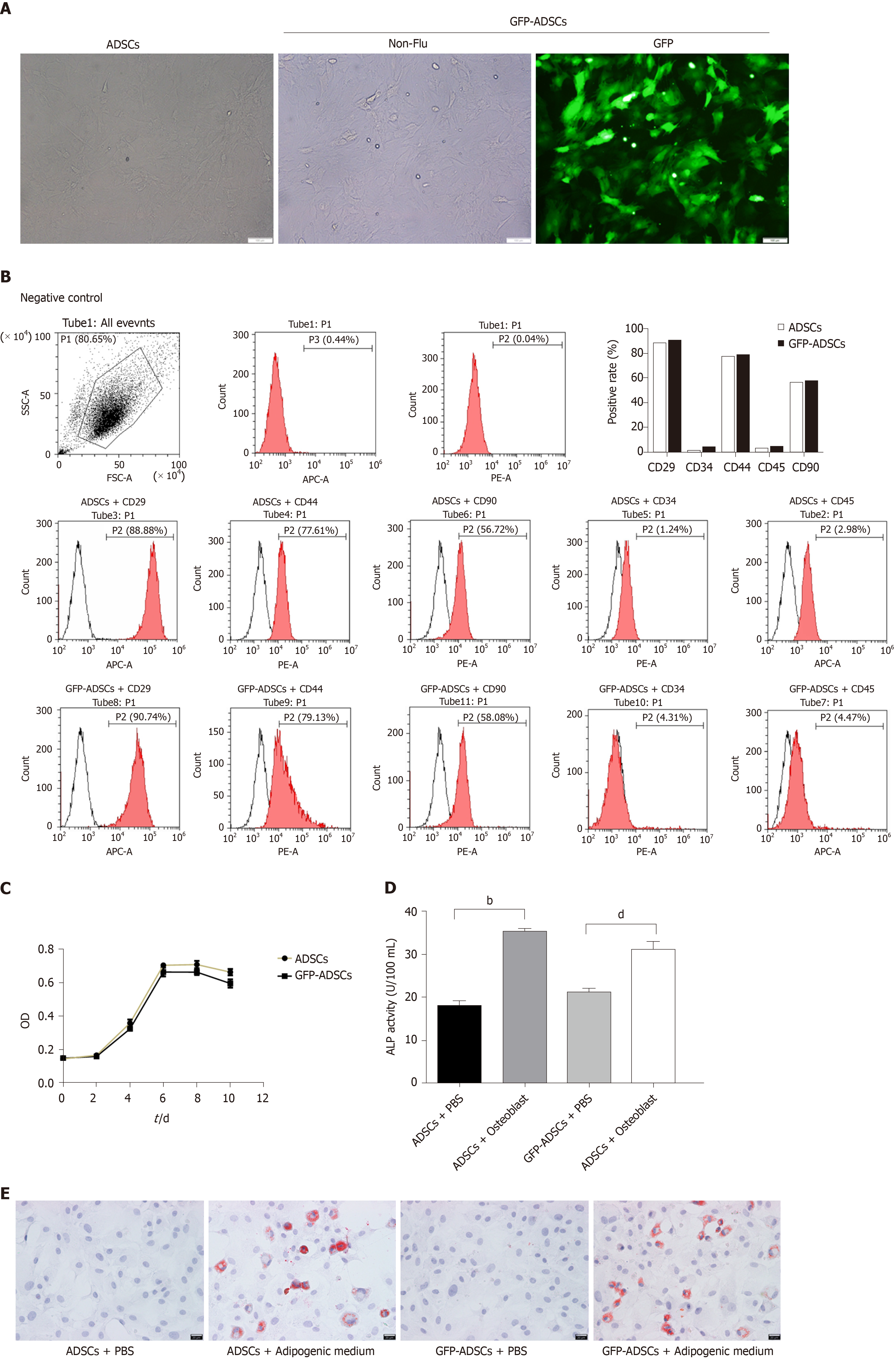
Figure 1 Isolation, culture, and identification of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Well-grown adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) were observed under a microscope (scale bar: 100 μm), and stable expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) was identified in GFP-ADSCs under a fluorescence microscope (scale bar: 100 μm); B: ADSC surface antigen analysis was carried out by flow cytometry. The characteristic surface biomarkers for ADSCs were confirmed, including CD29, CD44, and CD90 positivity and CD34 and CD45 negativity; C: ADSCs presented a typical S-like proliferation curve; D: Differentiation into osteocytes was confirmed by increased ALP. bP < 0.01 vs ADSCs + PBS, dP < 0.01 vs GFP-ADSCs + PBS; E: Differentiation into adipocytes was confirmed by the presence of lipid vesicles stained with oil red O (scale bar: 20 μm). ADSCs: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; GFP: Green fluorescent protein.
- Citation: Gao JG, Yu MS, Zhang MM, Gu XW, Ren Y, Zhou XX, Chen D, Yan TL, Li YM, Jin X. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate TNBS-induced colitis in rats by influencing intestinal epithelial cell regeneration, Wnt signaling, and T cell immunity. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(26): 3750-3766
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i26/3750.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i26.3750