Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2020; 26(25): 3577-3585
Published online Jul 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3577
Published online Jul 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3577
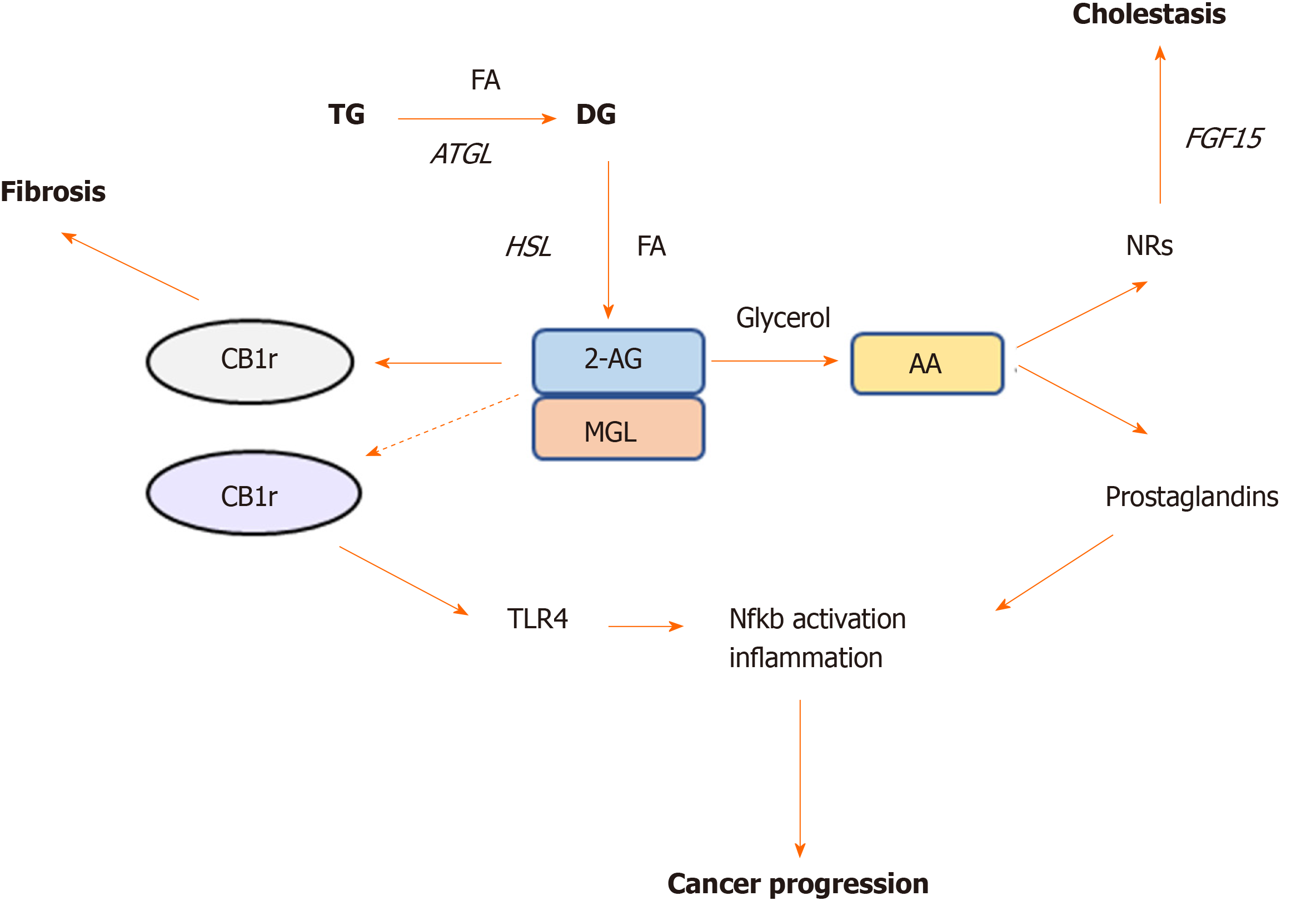
Figure 2 Monoacylglycerol lipase represent a crossroad between cannabinoid and lipid signaling pathways.
Monoacylglycerol lipase is the key enzyme degrading the endogenous cannabinoid ligand 2-AG, which in turn is able to bind either cannabinoid receptor (CB) -1r or -2r. Activation of CB1r was found to promote fibrosis whereas CB2r is involved in TLR4 activation and immune cells recruitment in cancer. Monoacylglycerol lipase action further hydrolyzes 2-AG into arachidonic acid, which is a precursor of prostaglandin synthesis, the main drivers of inflammation. Arachidonic acid was also found to bind nuclear receptors such as farnesoid X receptor and peroxisome proliferator activated receptors in the intestine and ameliorate cholestatic disease. AA: Arachidonic acid; NRs: Nuclear receptors; CB: Cannabinoid; MGL: Monoacylglycerol lipase; HSL: Hormone sensitive lipase; ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase; TG: Triglyceride; FA: Fatty acid.
- Citation: Tardelli M. Monoacylglycerol lipase reprograms lipid precursors signaling in liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(25): 3577-3585
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i25/3577.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3577