Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2020; 26(25): 3562-3576
Published online Jul 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3562
Published online Jul 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3562
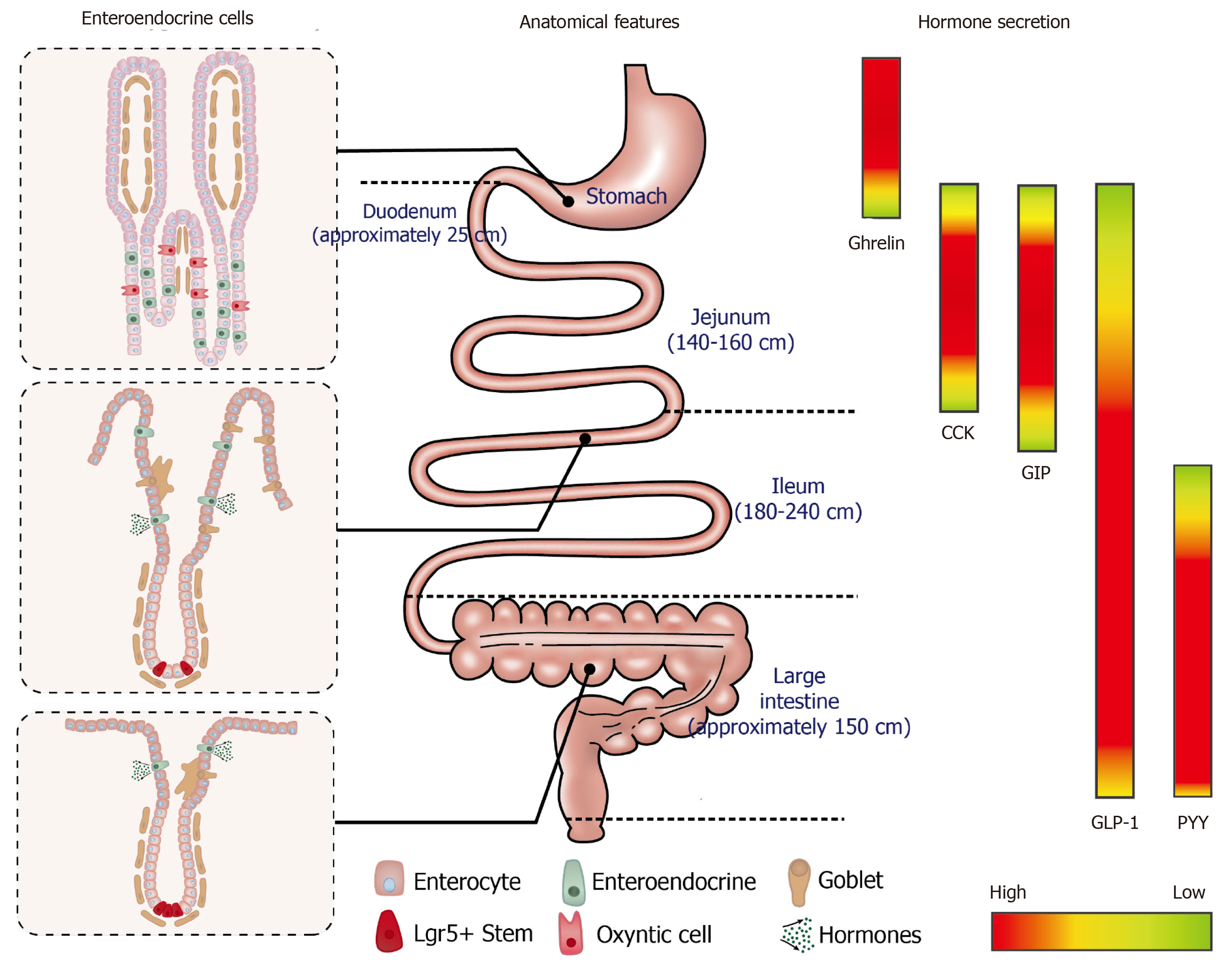
Figure 1 The composition of intestinal epithelial cells along the gastrointestinal tract (left); anatomical features and typical length of different sections of gastrointestinal tract (middle); regionally specific secretion profile of different gut hormones, including ghrelin, cholecystokinin, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide 1 and peptide YY (right).
CCK: Cholecystokinin; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1; GIP: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide; PYY: Peptide YY.
- Citation: Huang WK, Xie C, Young RL, Zhao JB, Ebendorff-Heidepriem H, Jones KL, Rayner CK, Wu TZ. Development of innovative tools for investigation of nutrient-gut interaction. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(25): 3562-3576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i25/3562.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3562