Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2020; 26(23): 3213-3224
Published online Jun 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3213
Published online Jun 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3213
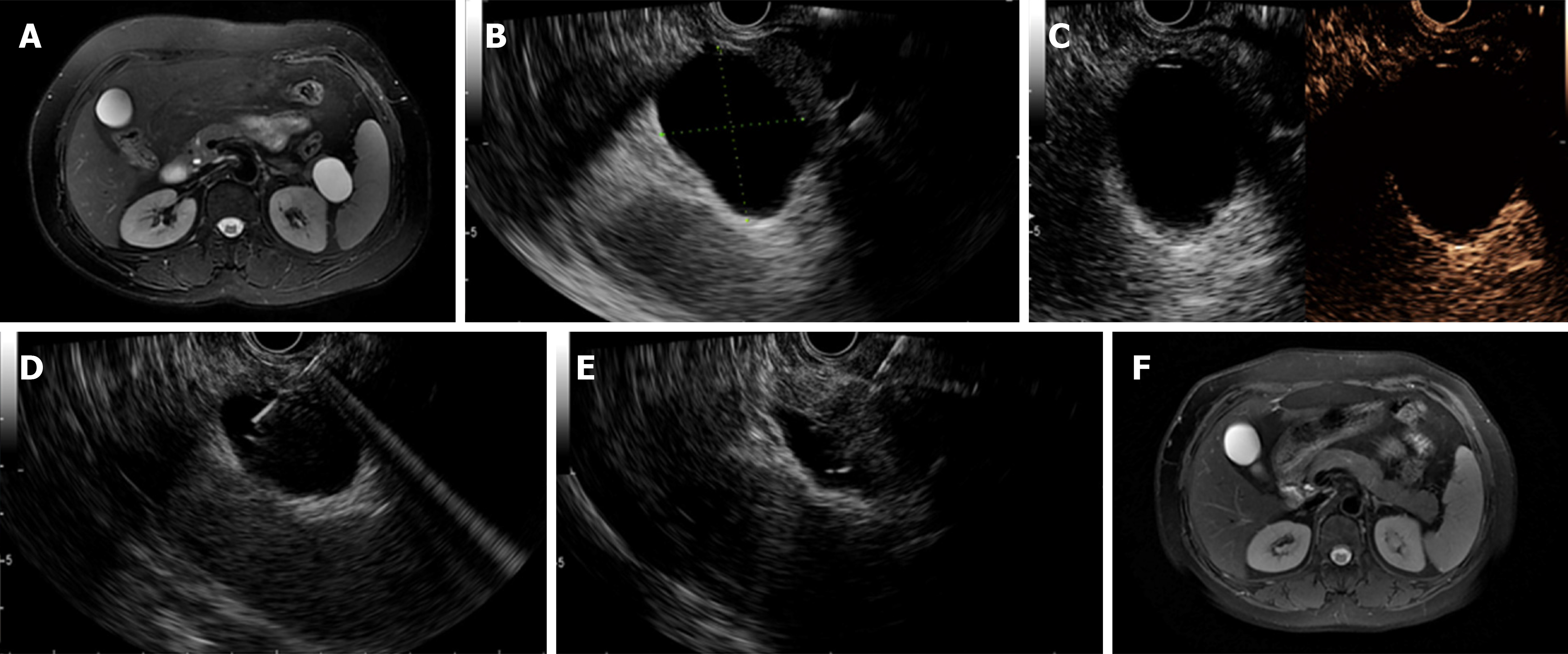
Figure 2 Complete resolution was achieved in a patient with a mucinous cystic neoplasm.
A: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before endoscopic ultrasound-guided (EUS-guided) ablation showing a 38.0 mm × 26.0 mm cyst located in the pancreatic body; B: EUS evaluation of the cyst showing a 37.0 mm × 32.0 mm cyst located in the pancreatic tail; C: Enhanced EUS view showing moderate enhancement of the cystic wall; D: EUS-guided fine needle aspiration to aspirate cyst fluid; E: Injection of the ablative agent through the needle; F. Follow-up MRI at 3 mo after ablation showing complete resolution. Used with permission from Chinese Journal of Digestive Endoscopy.
- Citation: Du C, Chai NL, Linghu EQ, Li HK, Feng XX. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided injective ablative treatment of pancreatic cystic neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(23): 3213-3224
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i23/3213.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3213