Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2020; 26(23): 3182-3200
Published online Jun 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3182
Published online Jun 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3182
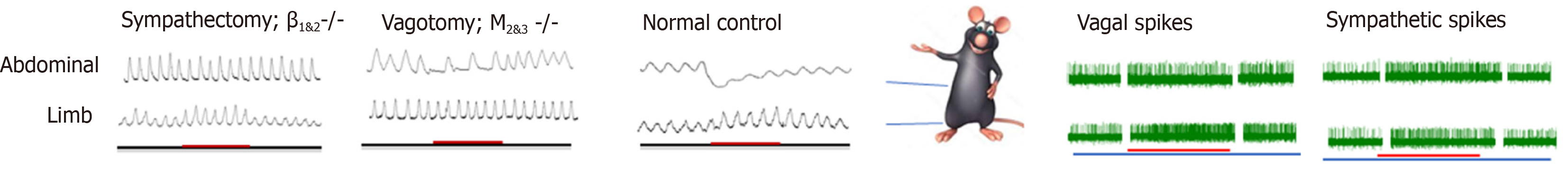
Figure 1 Regional-specific effect of acupuncture on gastrointestinal motility and its autonomic nervous system mechanism.
Stimulating the abdominal acupoints inhibits gastric/duodenal/jejunal motility by increasing sympathetic efferent fiber activity; and stimulating acupoints in the limb facilitates motility by exciting vagal efferent fiber activity. The effect of abdominal acupoints on gastrointestinal motility could be attenuated by sympathectomy or deletion of the gene encoding the β1&2 receptor. The effect of limbic acupoints on gastrointestinal motility could be attenuated by vagotomy or M2&3 receptor gene knock out.
- Citation: Yu Z. Neuromechanism of acupuncture regulating gastrointestinal motility. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(23): 3182-3200
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i23/3182.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3182