Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 3056-3075
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3056
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3056
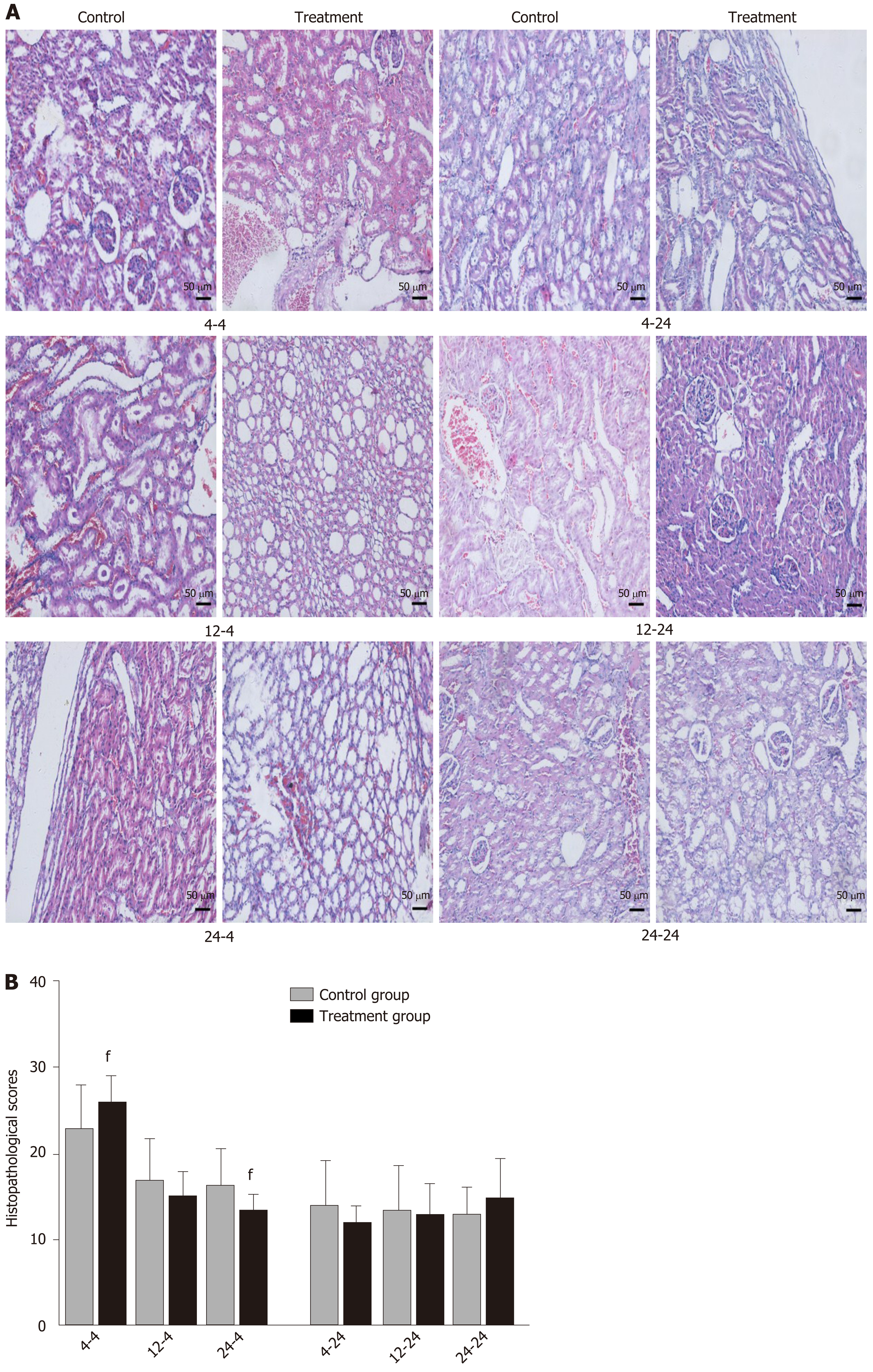
Figure 5 Pathological images and histopathological scores of kidney tissues in rats.
Rats in each treatment group were orally administered with Dachengqi decoction (DCQD), and rats in each control group were orally administered with normal saline. 4-4, 12-4, and 24-4: Rats were dosed with DCQD at 4 h, 12 h, and 24 h, respectively, after AP induction and were euthanized at 4 h after dosing. 4-24, 12-24, and 24-24: Rats were dosed with DCQD at 4 h, 12 h, and 24 h, respectively, after AP induction and were euthanized at 24 h after dosing. The kidney tissues were collected for pathological examination by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. A: Pathological images of the kidney (HE, × 200). B: Histopathological scores of heart injury. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 6). fP < 0.05 vs control group.
- Citation: Yao JQ, Zhu L, Miao YF, Zhu L, Chen H, Yuan L, Hu J, Yi XL, Wu QT, Yang XJ, Wan MH, Tang WF. Optimal dosing time of Dachengqi decoction for protection of extrapancreatic organs in rats with experimental acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 3056-3075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/3056.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3056