Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 3034-3055
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034
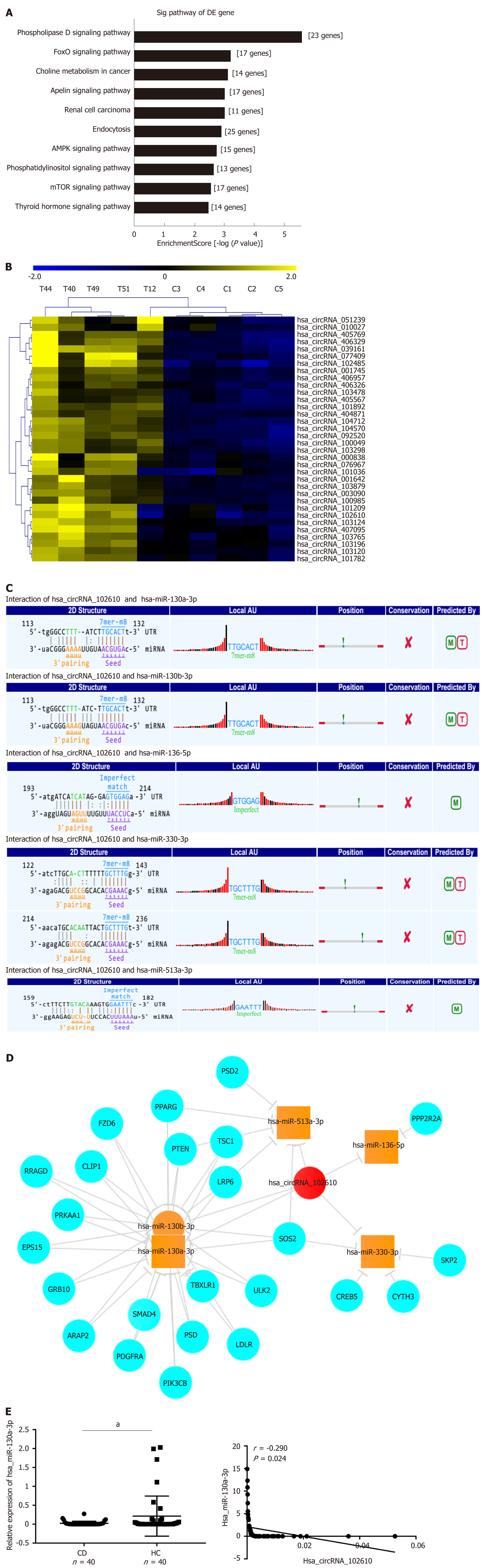
Figure 3 Functional prediction of hsa_circRNA_102610 by bioinformatics analysis.
A: Pathway analysis of the validated upregulated circRNAs (092520, 102610, 004662, and 103124) in Crohn’s disease (CD); B: Hierarchical clustering analysis of upregulated circRNAs in CD that might play roles in epithelial-mesenchymal transition according to miRNA response element analysis. Hsa_circRNA_102610 was included; C: miRNA response element analysis of hsa_circRNA_102610. Binding sites were predicted between hsa_circRNA_102610 and hsa-miR-130a-3p, hsa-miR-130b-3p, hsa-miR-136-5p, hsa-miR-330-3p, and hsa-miR-513a-3p. The databases miRanda and TargetScan were used for this prediction; D: Interaction network of hsa_circRNA_102610, the top 5 possibly binding miRNAs, and the corresponding proteins; E: Analysis of hsa-miR-130a-3p expression by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction and its correlation with hsa_circRNA_102610 expression in CD patients. aP < 0.05 vs healthy controls. CD: Crohn’s disease patients; HC: Healthy controls.
- Citation: Yin J, Ye YL, Hu T, Xu LJ, Zhang LP, Ji RN, Li P, Chen Q, Zhu JY, Pang Z. Hsa_circRNA_102610 upregulation in Crohn’s disease promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via sponging of hsa-miR-130a-3p. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 3034-3055
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/3034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034