Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 3034-3055
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034
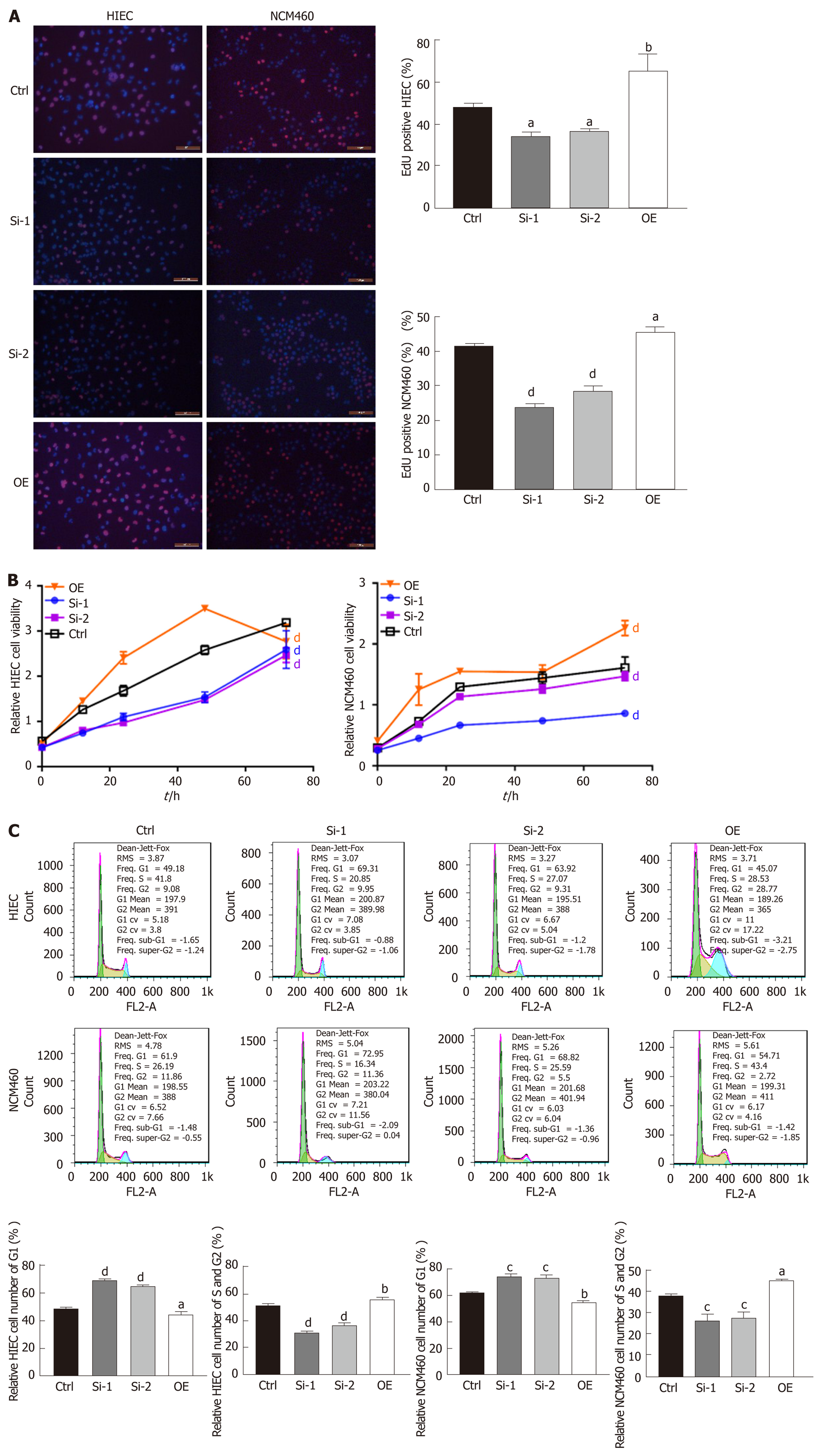
Figure 2 Hsa_circRNA_102610 overexpression promoted human intestinal epithelial cells and normal-derived colon mucosa cell line 460 cell proliferation.
A: 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine-staining of human intestinal epithelial cells. Red: 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine staining; blue: Hoechst 33342 staining; B: Relative HIEC and normal-derived colon mucosa cell line 460 cell viability, as measured by the cell counting kit-8 assay; C: Cell cycle phase detection for HIECs and normal-derived colon mucosa cell line 460 cells by flow cytometry. aP < 0.05 vs Ctrl, bP < 0.01 vs Ctrl, cP < 0.001 vs Ctrl, dP < 0.0001 vs Ctrl. Si-1 and Si-2: siRNAs mediating hsa_circRNA_102610 downregulation. OE: Hsa_circRNA_102610 overexpression by transient transfection. Ctrl: Control; HIECs: Human intestinal epithelial cells; NCM460: Normal-derived colon mucosa cell line 460; EdU: 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine.
- Citation: Yin J, Ye YL, Hu T, Xu LJ, Zhang LP, Ji RN, Li P, Chen Q, Zhu JY, Pang Z. Hsa_circRNA_102610 upregulation in Crohn’s disease promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via sponging of hsa-miR-130a-3p. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 3034-3055
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/3034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034