Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 3034-3055
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034
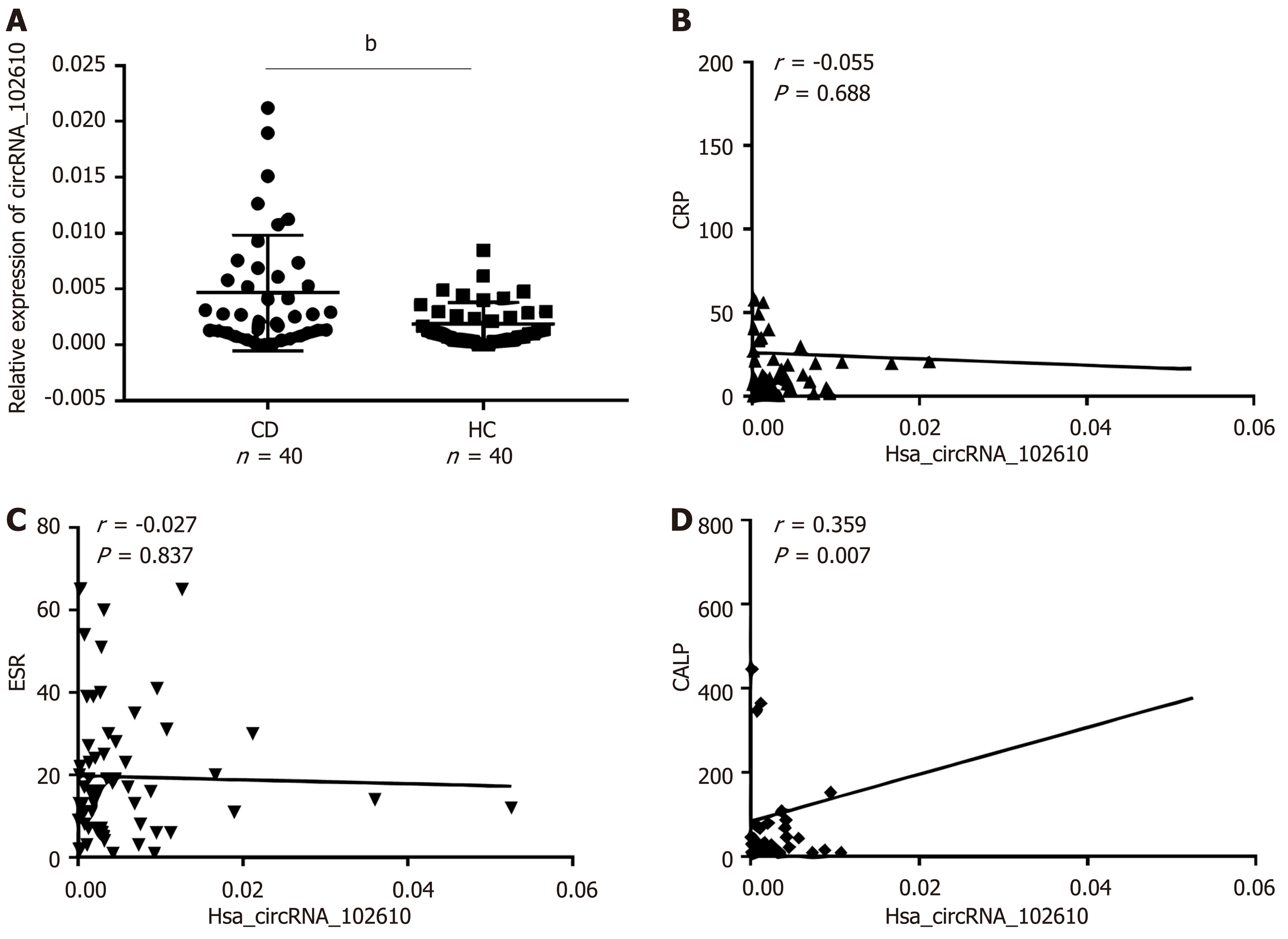
Figure 1 Correlation analysis between hsa_circRNA_102610 and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and calprotectin in Crohn’s disease patients.
A: Relative expression of hsa_circRNA_102610 in Crohn’s disease (CD) patients (n = 40) and healthy controls (HC, n = 40); B: Correlation analysis of hsa_circRNA_102610 and C-reactive protein in CD patients; C: Correlation analysis of hsa_circRNA_102610 and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in CD patients; D: Correlation analysis of hsa_circRNA_102610 and calprotectin in CD patients. bP < 0.01 vs HC. CRP: C-reactive protein; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CALP: Calprotectin; CD: Crohn’s disease.
- Citation: Yin J, Ye YL, Hu T, Xu LJ, Zhang LP, Ji RN, Li P, Chen Q, Zhu JY, Pang Z. Hsa_circRNA_102610 upregulation in Crohn’s disease promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via sponging of hsa-miR-130a-3p. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 3034-3055
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/3034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034