Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 2967-2986
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2967
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2967
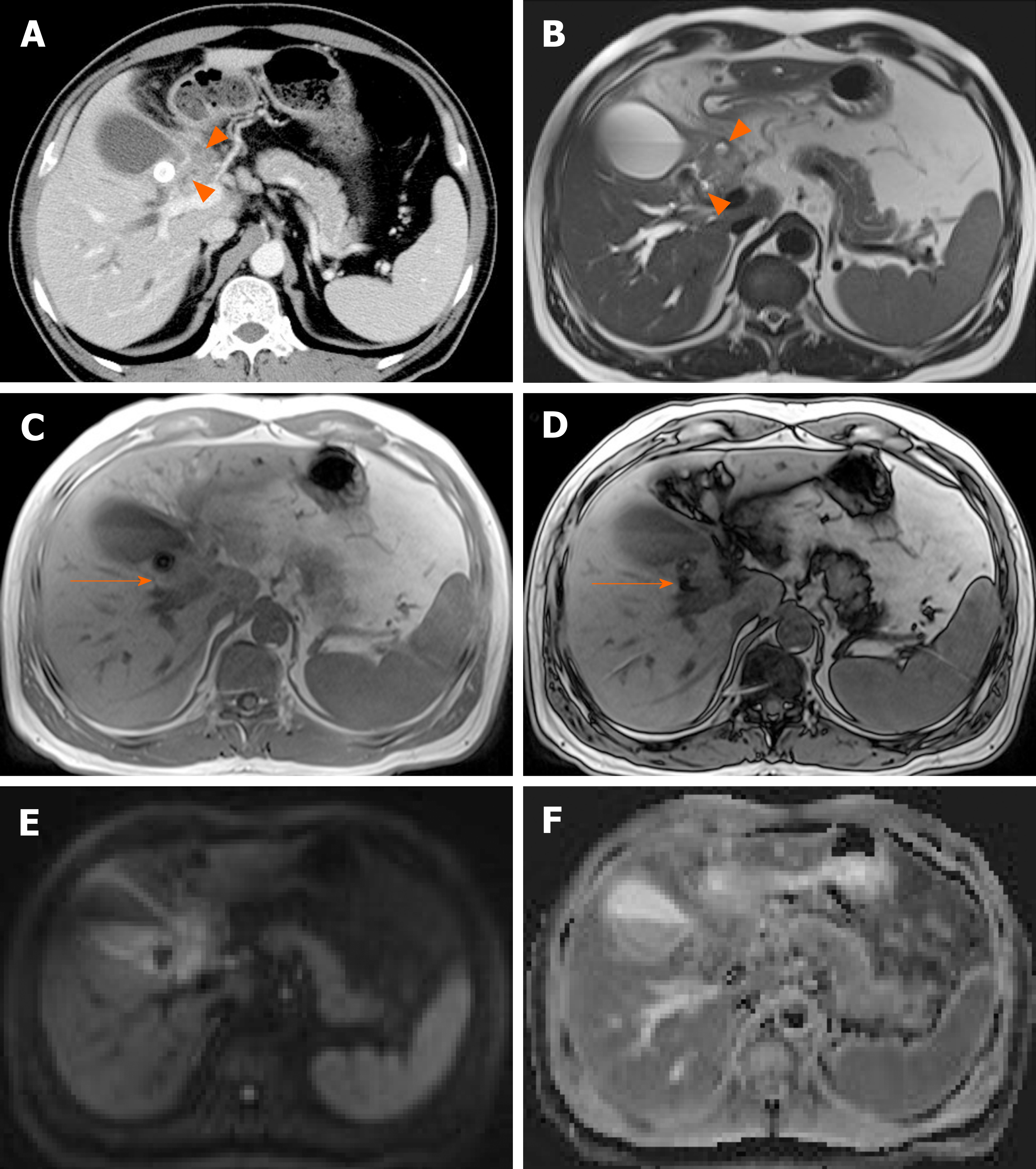
Figure 18 Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis.
A: Computed tomography scan of distended gallbladder with impacted gallstone at neck, showing segmental wall thickening of neck and proximal body and small hypodense intramural nodules (arrowheads); B: High signal intensity (arrowheads) of such abscesses or xanthogranulomas on T2-weighted image; C and D: Easily identifiable fat (arrow) within thickened wall by in-phase and opposed-phase chemical shift imaging; E and F: Mild diffusion restriction of wall thickening on diffusion-weighted imaging (E) and apparent diffusion coefficient map (F), less obvious than in gallbladder cancer.
- Citation: Yu MH, Kim YJ, Park HS, Jung SI. Benign gallbladder diseases: Imaging techniques and tips for differentiating with malignant gallbladder diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 2967-2986
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/2967.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2967