Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 2889-2901
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2889
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2889
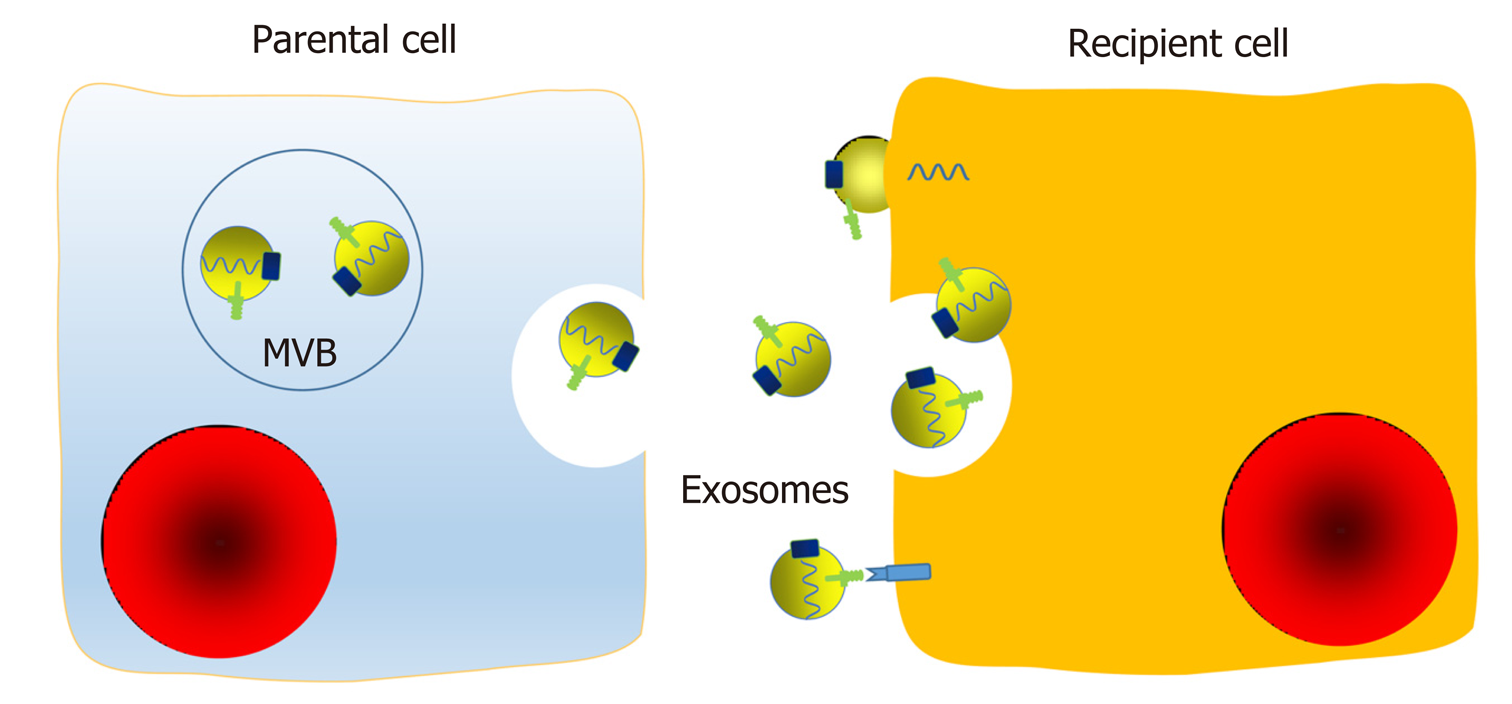
Figure 3 Mechanisms of transfer of exosomal components between cells.
Exosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles that are released from their parental cell membrane by shedding or budding of multivesicular bodies. Exosomes contain a set of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Exosomes can interact with surface membrane molecules, fuse with the recipient cell membrane directly, or be endocytosed in a nonselective way to transfer their inner components. In addition, exosomes can release small aggregates or be cleaved by proteases, and then be taken up via a phagocytic mechanism by neighboring cells or act as ligands. Therefore, exosomes may regulate functions of neighboring cells and distant cells by means of autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine mechanisms, as a novel communication method between cells. MVB: Multivesicular bodies.
- Citation: Lv J, Zhao HP, Dai K, Cheng Y, Zhang J, Guo L. Circulating exosomal miRNAs as potential biomarkers for Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 2889-2901
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/2889.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2889