Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2810-2820
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2810
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2810
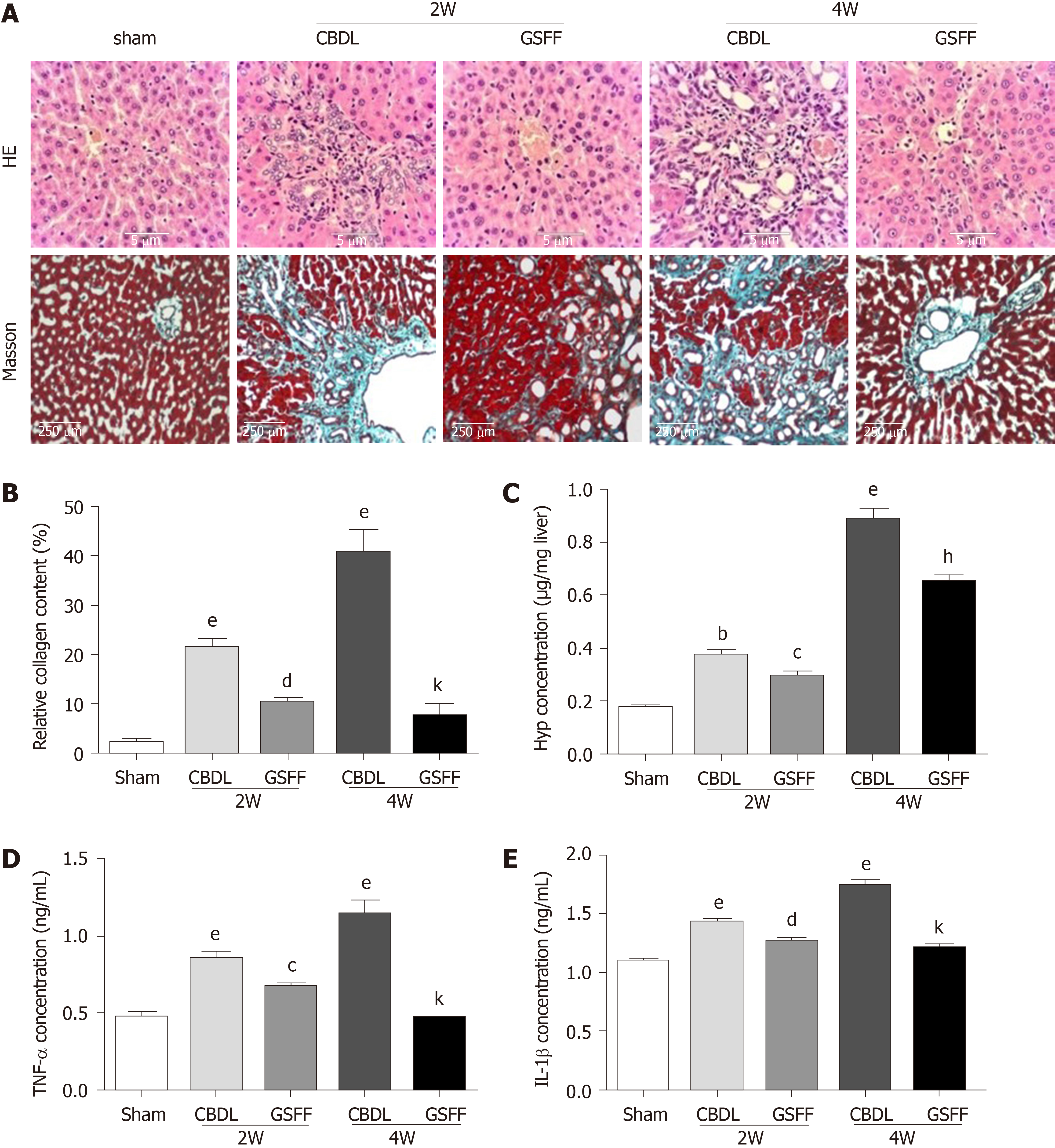
Figure 2 Gan Shen Fu Fang inhibited liver fibrosis and alleviated the inflammatory response.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Masson staining of the liver tissue; B: The collagen content was measured by quantitative histomorphometry; C: Hydroxyproline concentration in the liver; D and E: Tumour necrosis factor-α and IL-1β levels in the liver. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, compared with the sham group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, compared with the 2W-CBDL rats; hP < 0.01, kP < 0.001, compared with the 4W-CBDL rats. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; CBDL: Common bile duct-ligated; GSFF: Gan Shen Fu Fang; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; Hyp: Hydroxyproline.
- Citation: Du QH, Zhang CJ, Li WH, Mu Y, Xu Y, Lowe S, Han L, Yu X, Wang SY, Li Y, Li J. Gan Shen Fu Fang ameliorates liver fibrosis in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the inflammatory response and extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2810-2820
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2810.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2810