Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2758-2767
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758
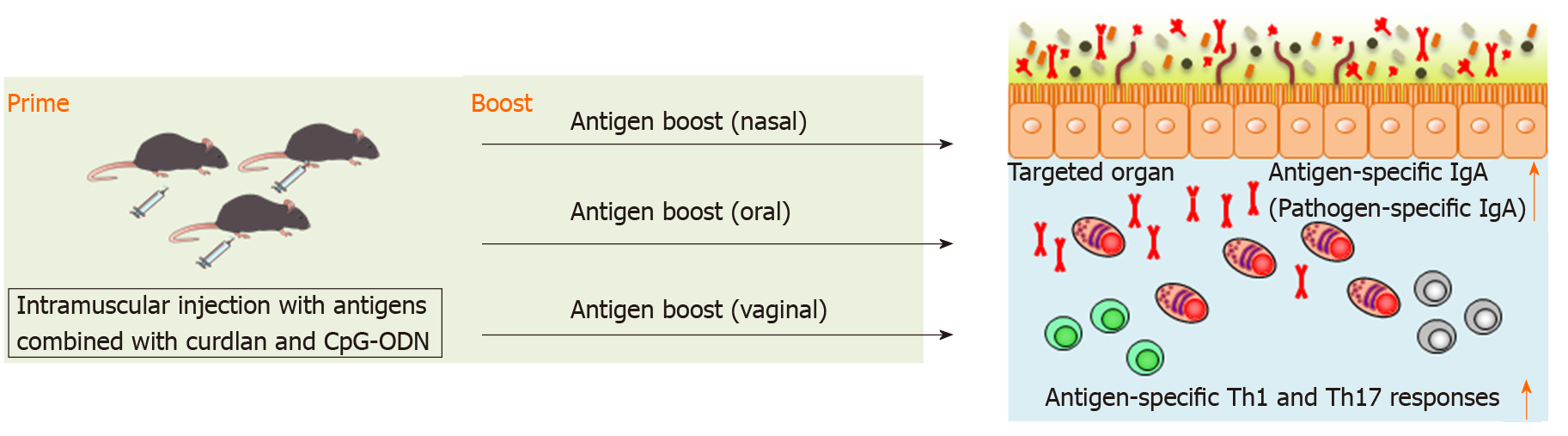
Figure 2 Scheme of antigen-specific immune responses by prime–boost vaccination.
Parenteral immunization with antigen emulsified in curdlan and CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides induces antigen-specific fecal IgA as well as serum IgG and splenic Th1 and Th17 responses. Once primed, high titers of long-lasting antigen-specific lung, intestinal, or vaginal IgA are induced after nasal, oral, or vaginal antigen administration, respectively. Also, antigen-specific Th1 and Th17 responses are induced at the targeted organs. CpG-ODN: CpG oligodeoxynucleotides.
- Citation: Fujimoto K, Uematsu S. Vaccine therapy for dysbiosis-related diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2758-2767
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2758.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758