Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2758-2767
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758
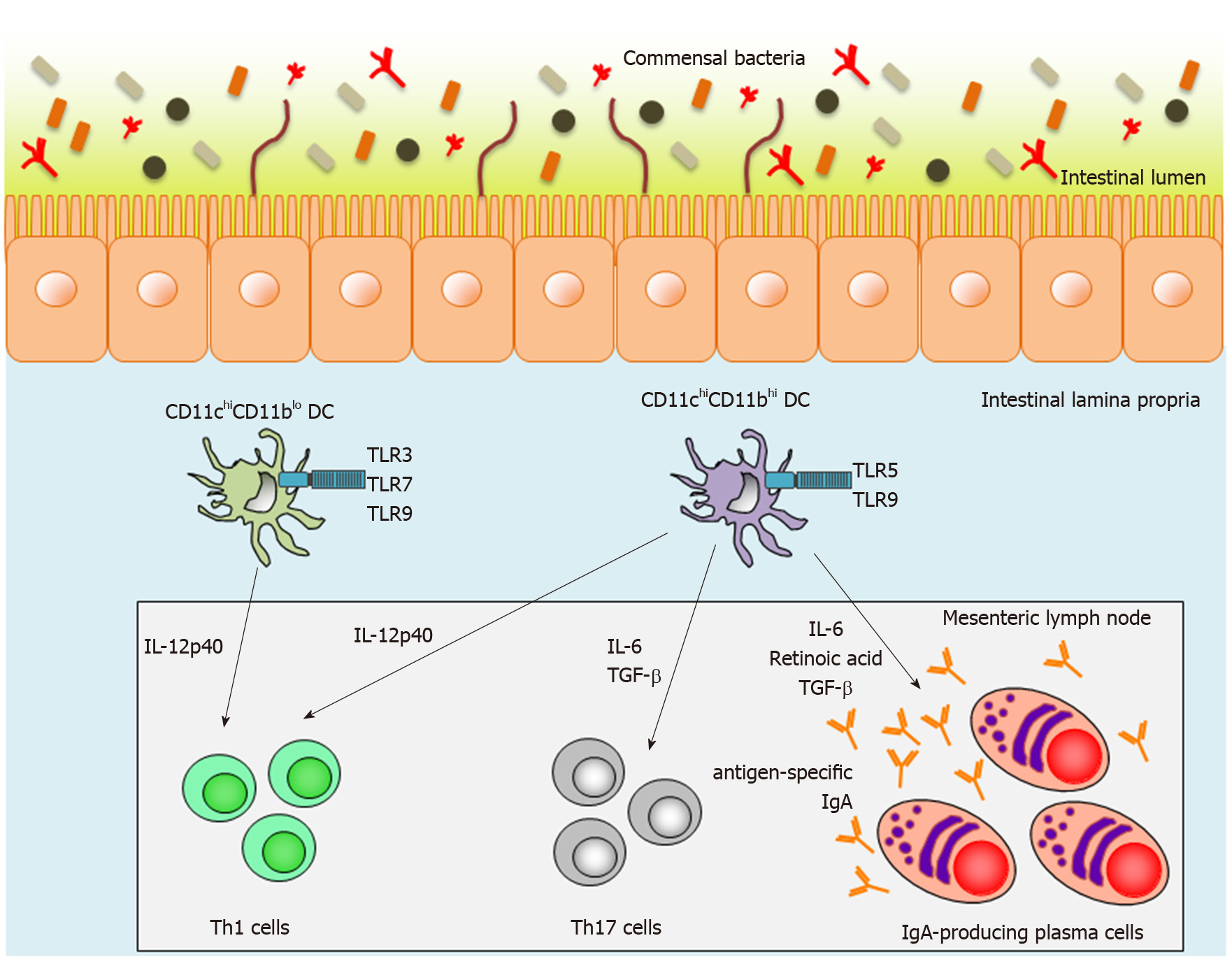
Figure 1 Function of two distinct lamina propria dendritic cells in the small intestine.
Mouse small-intestinal lamina propria dendritic cells (LPDCs) are divided into two subsets on the basis of CD11c and CD11b expression. CD11chiCD11blo LPDCs express Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3, TLR7 and TLR9, whereas CD11chiCD11bhi LPDCs express TLR5 and TLR9. After TLR stimulation, activated CD11chiCD11bhi LPDCs can produce interleukin (IL)-12p40, IL-6, transforming growth factor-β and retinoic acid, and subsequently induce antigen-specific Th1 and Th17 responses and antigen-specific-IgA-producing plasma cells. In contrast to CD11chiCD11bhi LPDCs, activated CD11chiCD11blo LPDCs can induce antigen-specific Th1 responses, but not antigen-specific Th17 responses and antigen-specific-IgA-producing plasma cells. TLR: Toll-like receptor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; IL: Interleukin; DC: Dendritic cell.
- Citation: Fujimoto K, Uematsu S. Vaccine therapy for dysbiosis-related diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2758-2767
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2758.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2758