Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2020; 26(19): 2374-2387
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2374
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2374
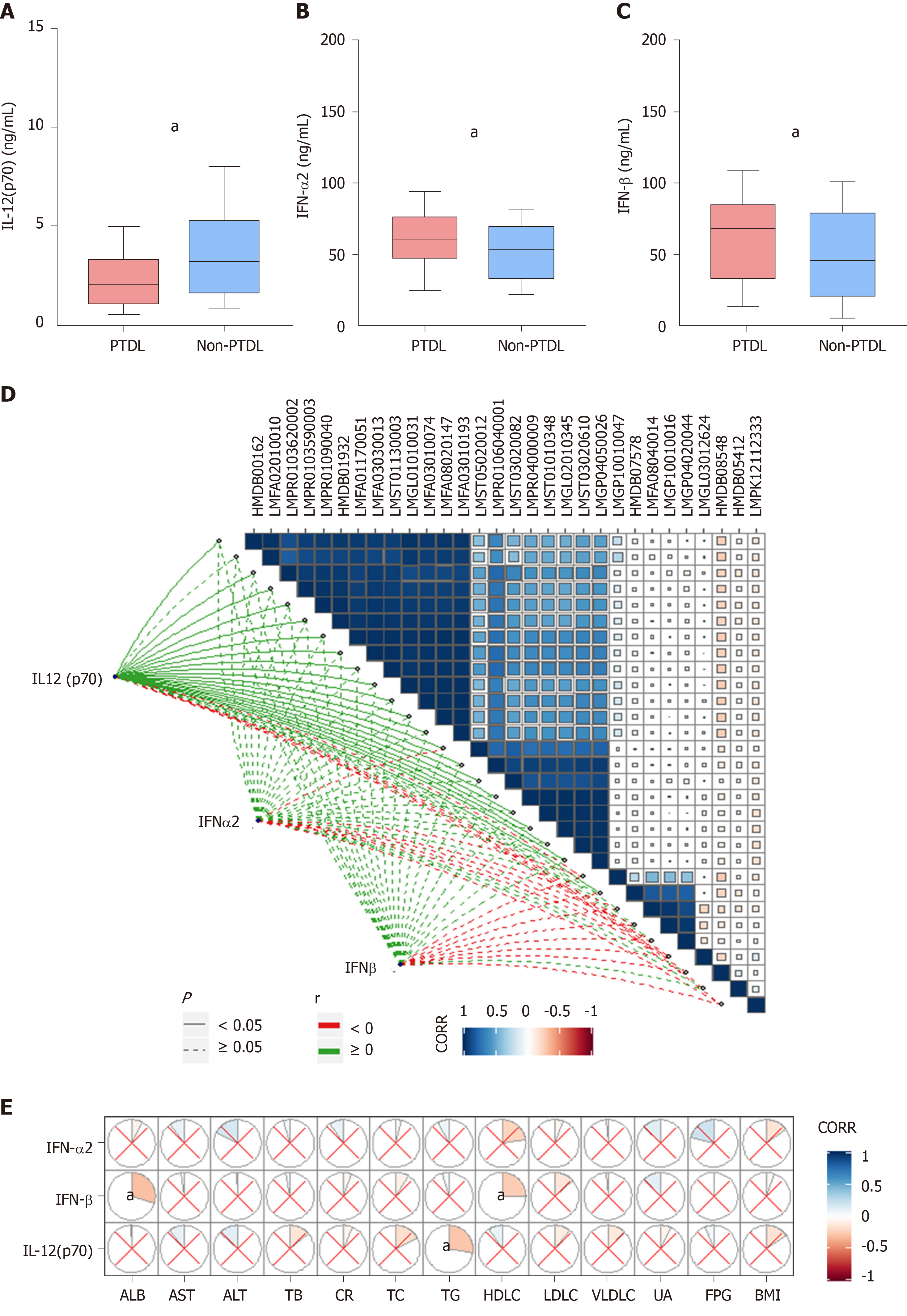
Figure 4 Peripheral cytokine profile of post-transplant dyslipidemia and non-post-transplant dyslipidemia groups.
A-C: The interleukin (IL)-12 (p70), IFN-α2, and IFN-β levels were significantly differentially expressed between post-transplant dyslipidemia group and non-post-transplant dyslipidemia group; D: Correlations between differential cytokines and metabolic profiles; E: Correlation between differential cytokines and recipients’ pre-transplant clinical metabolic parameters. aP < 0.05. PTDL: Post-transplant dyslipidemia; ALB: Albumin; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TB: Total bilirubin; CR: Creatinine; TC: Total cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride; HDLC: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLC: Low density lipoprotein cholesterol; VLDLC: Very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; UA: Uric acid; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; BMI: Body mass index; CORR: Correlation.
- Citation: Huang HT, Zhang XY, Zhang C, Ling Q, Zheng SS. Predicting dyslipidemia after liver transplantation: A significant role of recipient metabolic inflammation profile. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(19): 2374-2387
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i19/2374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2374