Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2020; 26(19): 2349-2373
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2349
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2349
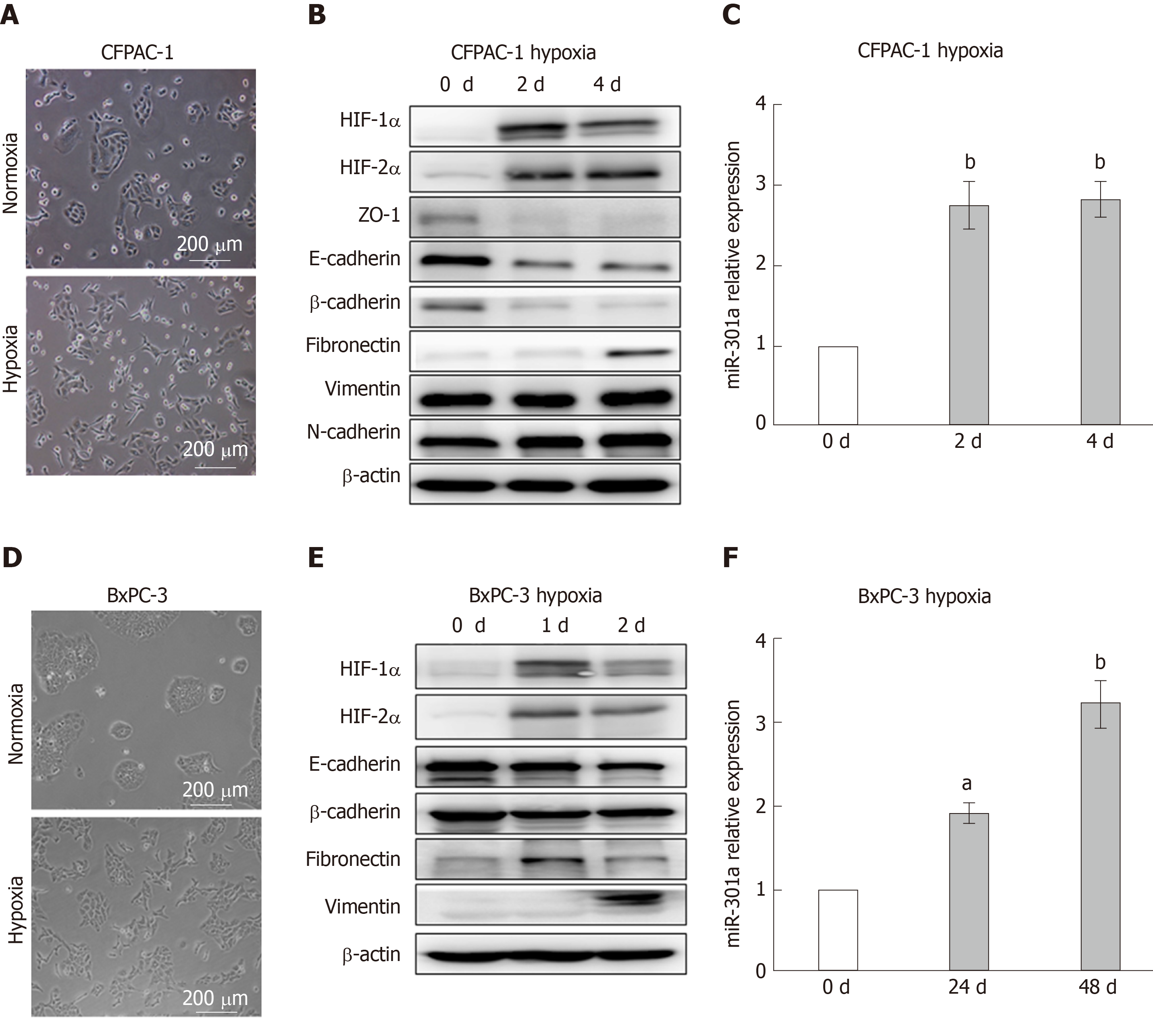
Figure 1 Hypoxia induces pancreatic cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases miR-301a expression.
A and D: Phase-contrast photomicrographs. Notably, CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells cultured under normoxia exhibit a typical epithelial morphology, whereas cells cultured under hypoxia for 48 h exhibit a typical mesenchymal morphology; B and E: Western blot analysis was performed to detect hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, HIF-2α, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers. The expression levels of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and the mesenchymal markers (Vimentin and Fibronectin) in hypoxia-cultured CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells were higher than the levels in normoxia-cultured cells, while the expression levels of the epithelial markers (E-cadherin and β-catenin) were lower under hypoxia than under normoxia; C and F: qRT-PCR was used to measure the expression of miR-301a. The expression of miR-301a was higher in hypoxia-cultured CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells than in the normoxia-cultured cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor.
- Citation: Zhang KD, Hu B, Cen G, Yang YH, Chen WW, Guo ZY, Wang XF, Zhao Q, Qiu ZJ. MiR-301a transcriptionally activated by HIF-2α promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting TP63 in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(19): 2349-2373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i19/2349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2349