Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2020; 26(18): 2247-2267
Published online May 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2247
Published online May 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2247
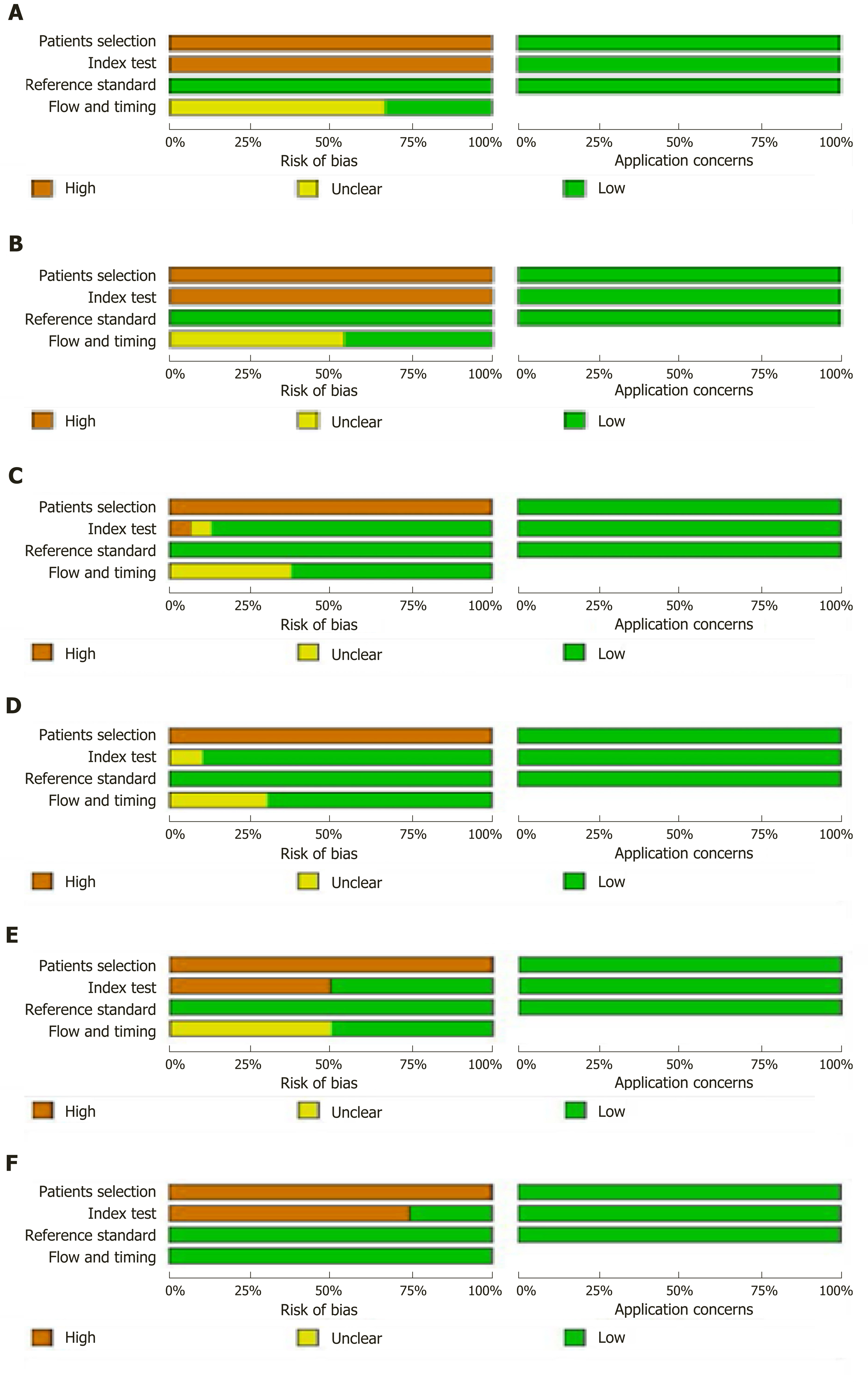
Figure 2 Methodological evaluation according to Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 of the included articles.
A, C, and E: Diagnosis of esophageal varices using liver stiffness measurement, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, respectively; B, D, and F: Prediction of high-bleeding-risk esophageal varices using liver stiffness measurement, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, respectively. Articles were identified as having a potential bias risk for patient selection and index text.
- Citation: Li Y, Li L, Weng HL, Liebe R, Ding HG. Computed tomography vs liver stiffness measurement and magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(18): 2247-2267
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i18/2247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2247