Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2020; 26(17): 2119-2125
Published online May 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i17.2119
Published online May 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i17.2119
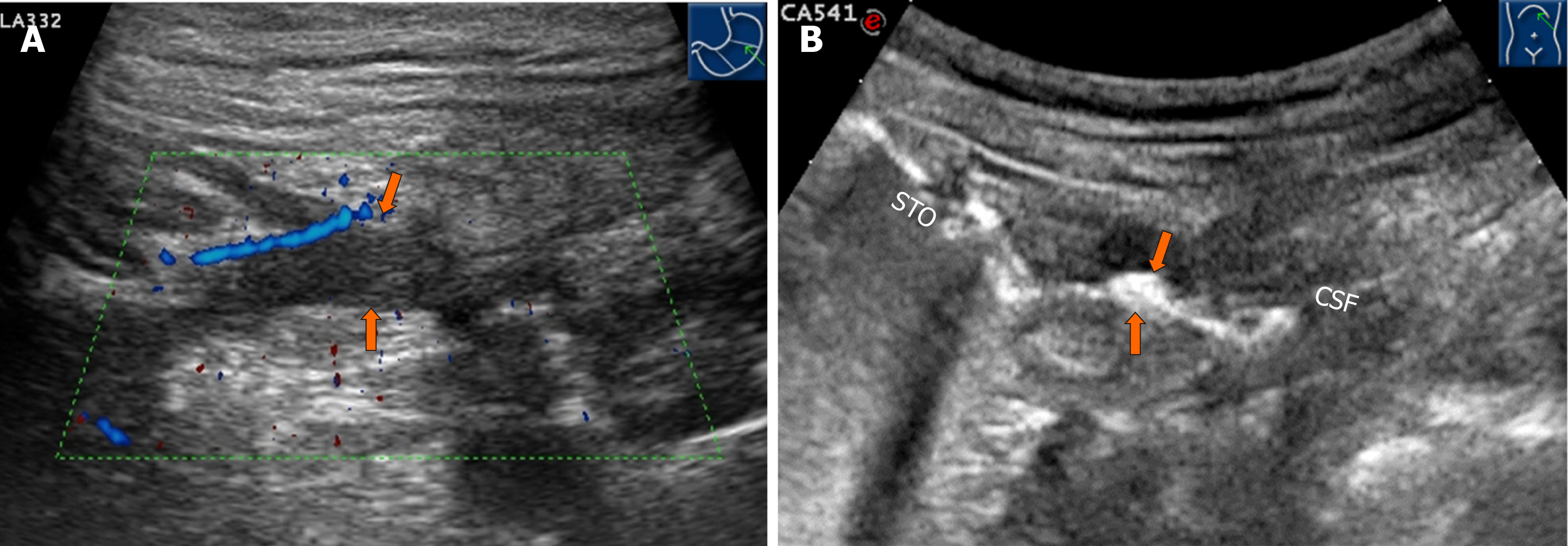
Figure 3 Ultrasound.
A: Transverse Doppler sonogram through the stomach demonstrating the hypoechoic fistula wall at the section of the short axis of the stomach (orange arrows). Limberg grade II blood signals can be observed. B: Oral agent contrast-enhanced ultrasound showing the hyperechoic gas passage connecting the splenic flexure of the colon to the greater curvature of the stomach (orange arrows).
- Citation: Wu S, Zhuang H, Zhao JY, Wang YF. Gastrocolic fistula in Crohn’s disease detected by oral agent contrast-enhanced ultrasound: A case report of a novel ultrasound modality. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(17): 2119-2125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i17/2119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i17.2119