Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2020; 26(15): 1758-1774
Published online Apr 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1758
Published online Apr 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1758
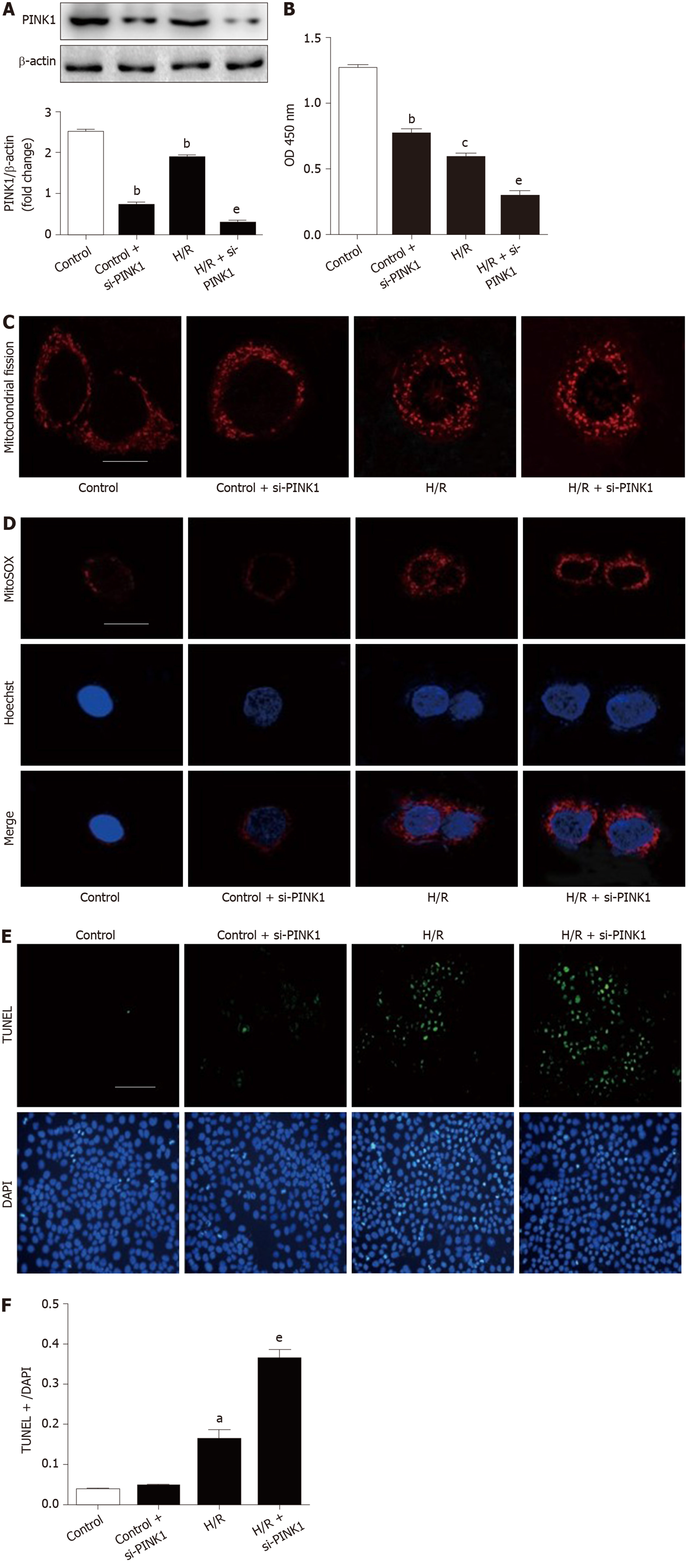
Figure 5 Inhibition of PTEN-induced kinase 1 aggravates mitochondrial fission, reactive oxygen species accumulation and apoptosis in Caco-2 hypoxia/reoxygenation cells.
A: The protein expression of PTEN- induced kinase 1 (PINK1) by Western blotting after PINK1 Small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection (n = 3); B: Cell viability was detected by CCK-8 assay (n = 6); C: Deep Red FM in Caco-2 cells (scale bar = 10 μm); D: MitoSOX assay in Caco-2 cells (scale bar = 10 μm); E: PINK1 siRNA transfection increases intestinal cell apoptosis according to a TUNEL assay (length of the bar scale: 100 μm); F: PINK1 siRNA transfection increased intestinal cell apoptosis, as shown by the TUNEL positive cell ratio (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 compared with the control group; eP < 0.01 compared with the H/R group. DRP1: Dynamin-related protein 1; PINK1: PTEN induced kinase 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; CCK-8: Cell Counting Kit-8; H/R: Hypoxia/reoxygenation; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; TUNEL: Terminal-deoxynucleoitidyl Transferase Mediated Nick End Labeling; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Qasim W, Li Y, Sun RM, Feng DC, Wang ZY, Liu DS, Yao JH, Tian XF. PTEN-induced kinase 1-induced dynamin-related protein 1 Ser637 phosphorylation reduces mitochondrial fission and protects against intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(15): 1758-1774
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i15/1758.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1758