Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2020; 26(14): 1601-1612
Published online Apr 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i14.1601
Published online Apr 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i14.1601
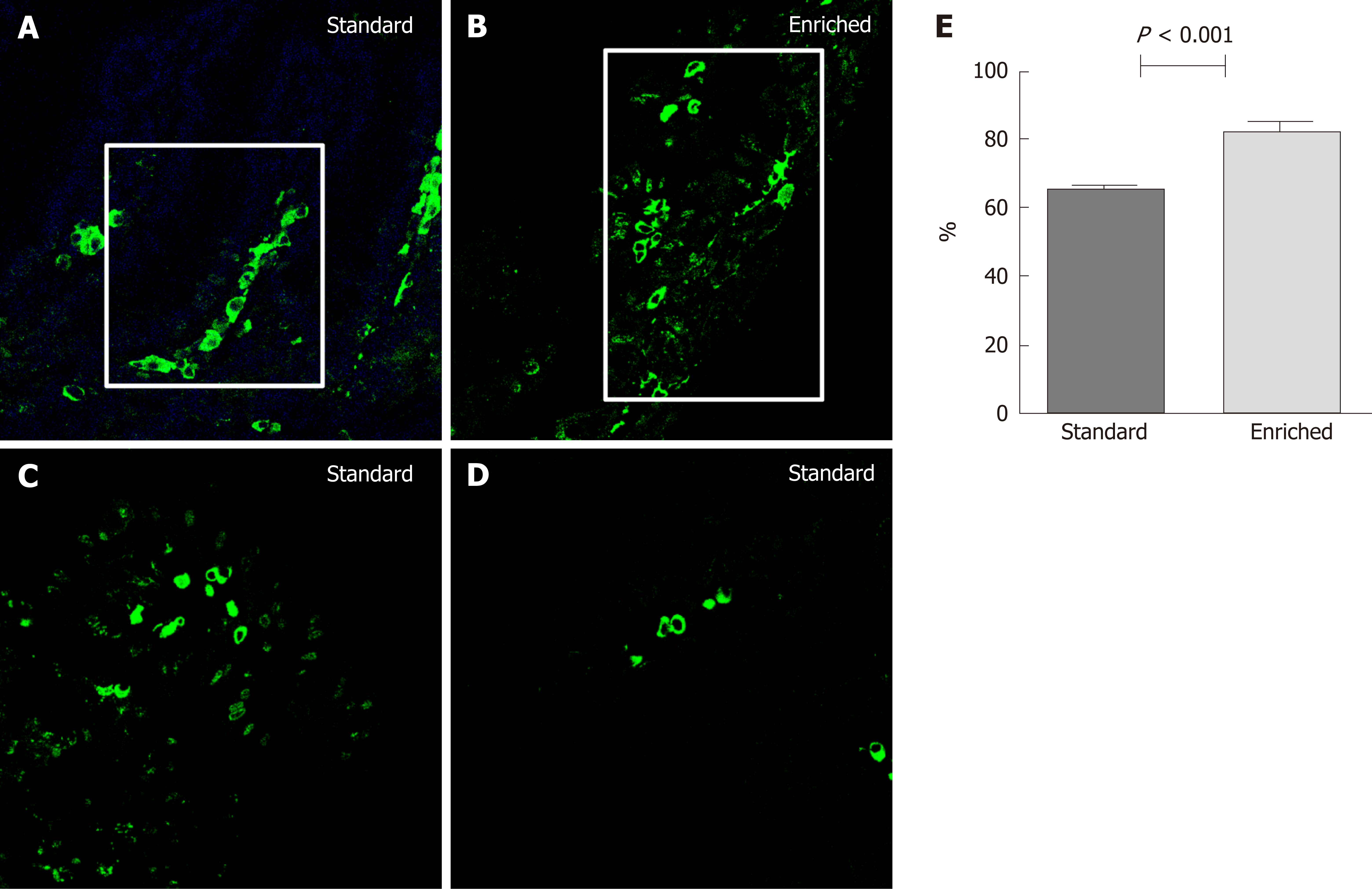
Figure 3 The percentage of villous axis covered by the highest labeled cell at the 48th h after injection in normal mucosa.
A, B: Percentage of villous area covered by the highest bromodeoxyuridine labeled cell at the 48th h after injection in normal colonic mucosa in standard (A) and enriched diet group (B); C, D: The pictures at 72th (C) and 96th (D) h in standard group is represented; the findings at these times were the same in the enriched diet group and limited to the tip of villi. Positive cells are stained green (confocal microscopy; magnification: 630 ×); E: Quantitative analysis.
- Citation: Girardi B, Pricci M, Giorgio F, Piazzolla M, Iannone A, Losurdo G, Principi M, Barone M, Ierardi E, Di Leo A. Silymarin, boswellic acid and curcumin enriched dietetic formulation reduces the growth of inherited intestinal polyps in an animal model. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(14): 1601-1612
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i14/1601.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i14.1601