Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2020; 26(13): 1439-1449
Published online Apr 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i13.1439
Published online Apr 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i13.1439
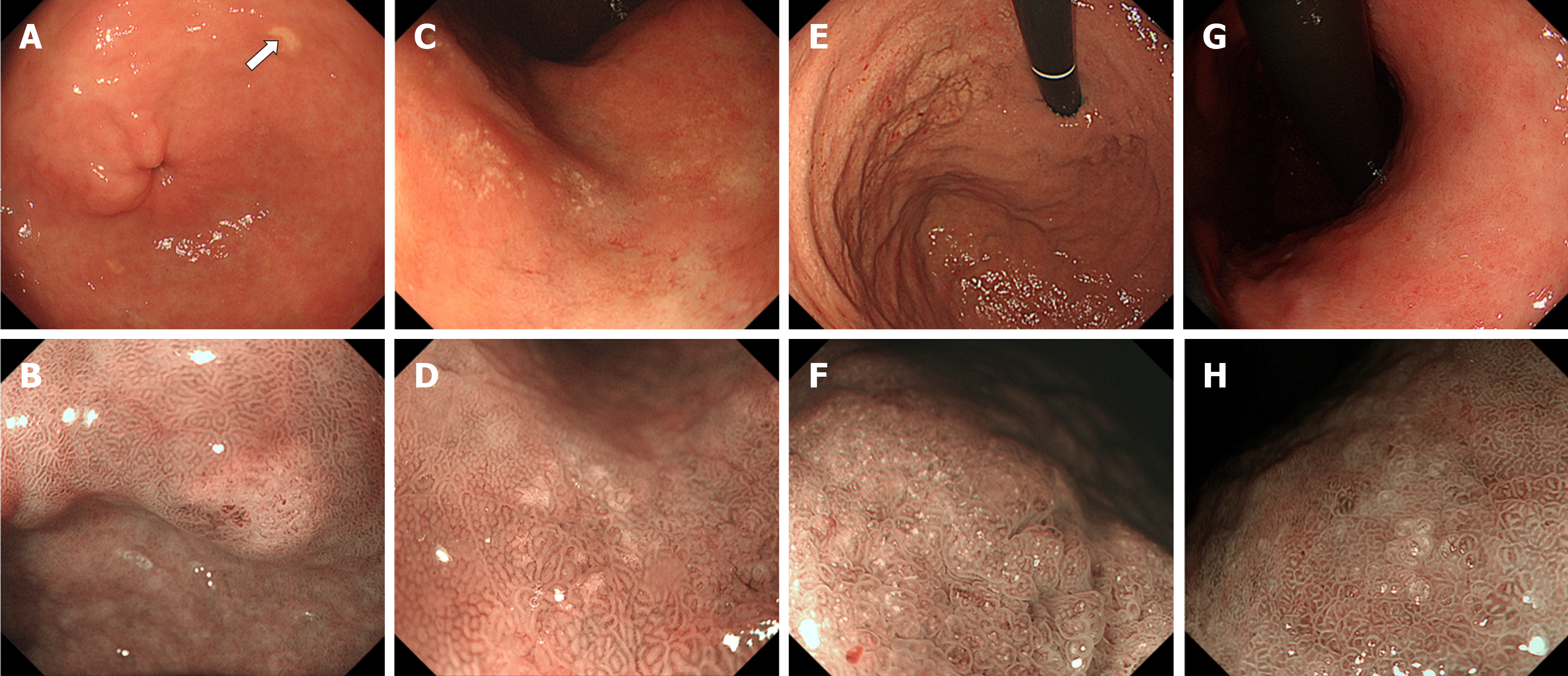
Figure 4 Typical endoscopic features of gastric lanthanum deposition during conventional white-light (upper row) and magnified observation with narrow-band imaging (lower row).
A, B: “Whitish spot” is defined as a whitish lesion ≤ 20 mm in diameter with a uniform white color; C, D: “Annular whitish mucosa” are lesion (s) ≤ 20 mm in diameter with white color in the periphery; E, F: “Diffuse whitish mucosa” appears with a white area > 20 mm in diameter; G, H: “Fine granular whitish deposition” is a tiny or faint whitish lesion (s) ≤ 1 mm in diameter.
- Citation: Iwamuro M, Urata H, Tanaka T, Okada H. Review of the diagnosis of gastrointestinal lanthanum deposition. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(13): 1439-1449
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i13/1439.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i13.1439