Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2020; 26(10): 1029-1041
Published online Mar 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i10.1029
Published online Mar 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i10.1029
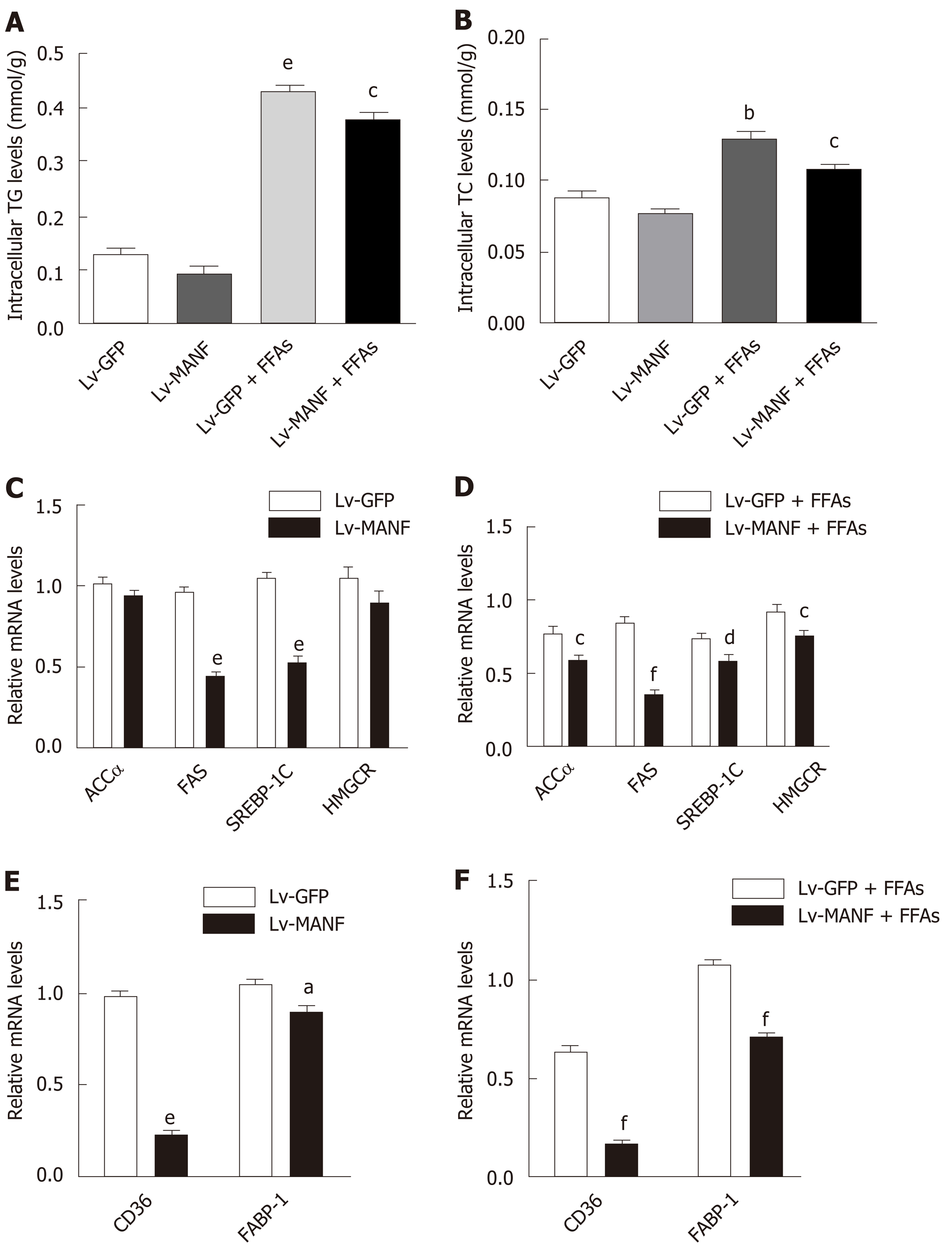
Figure 3 Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor overexpression suppresses lipogenesis.
A and B: The intracellular levels of TG (A) and TC (B) in HepG2 cells treated with bovine serum albumin or free fatty acids (FFAs) for 72 h, bP<0.01, eP < 0.001 vs Lv-GFP; cP < 0.05 vs Lv-GFP + FFAs; C and D: The mRNA levels of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis (ACCα, FAS, SREBP-1C, and HMGCR) without FFAs treatment (C) and upon FFAs treatment (D), eP < 0.001 vs Lv-GFP; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs Lv-GFP + FFAs; E and F: The mRNA levels of genes related to lipid uptake (CD36, FABP-1) without FFAs treatment (E) and upon FFAs treatment (F), aP < 0.05, eP < 0.001 vs Lv-GFP; fP < 0.001 vs Lv-GFP + FFAs. Data represent the mean ± SE, and all experiments were repeated three times. MANF: Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol; Lv: Lentivirus; BSA: Bovine serum albumin; FFAs: Free fatty acids; ACCα: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase α; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; SREBP-1C: Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1C; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; FABP-1: Fatty acid binding protein-1.
- Citation: He M, Wang C, Long XH, Peng JJ, Liu DF, Yang GY, Jensen MD, Zhang LL. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates steatosis in HepG2 cells by regulating hepatic lipid metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(10): 1029-1041
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i10/1029.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i10.1029