Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2020; 26(1): 55-69
Published online Jan 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.55
Published online Jan 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.55
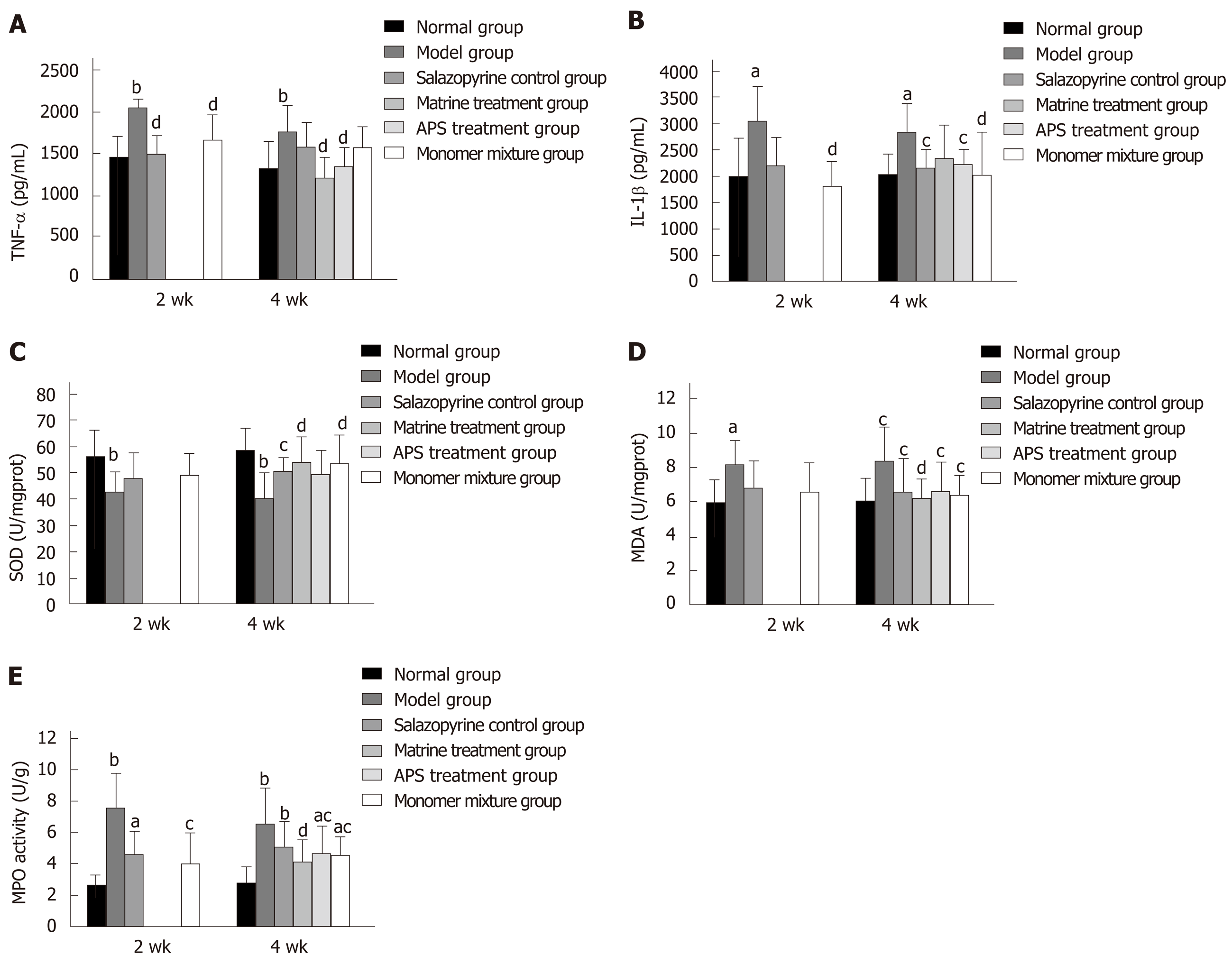
Figure 5 Astragalus polysaccharides combined with matrine relieve inflammatory response and oxidative stress injury in lung tissues of rats with ulcerative colitis.
A and B: Tumor necrosis factor-α (A) and interleukin-1β levels (B) in lung tissues in various groups detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); C-E: Activities of superoxide dismutase (C), malondialdehyde (D), and myeloperoxidase (E) in lung tissues in various groups determined with commercial detection kits. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs normal group; cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs model group. APS: Astragalus polysaccharides; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β: Interleukins-1β; MPO: Myeloperoxidase.
- Citation: Yan X, Lu QG, Zeng L, Li XH, Liu Y, Du XF, Bai GM. Synergistic protection of astragalus polysaccharides and matrine against ulcerative colitis and associated lung injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(1): 55-69
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i1/55.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.55