Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2020; 26(1): 35-54
Published online Jan 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.35
Published online Jan 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.35
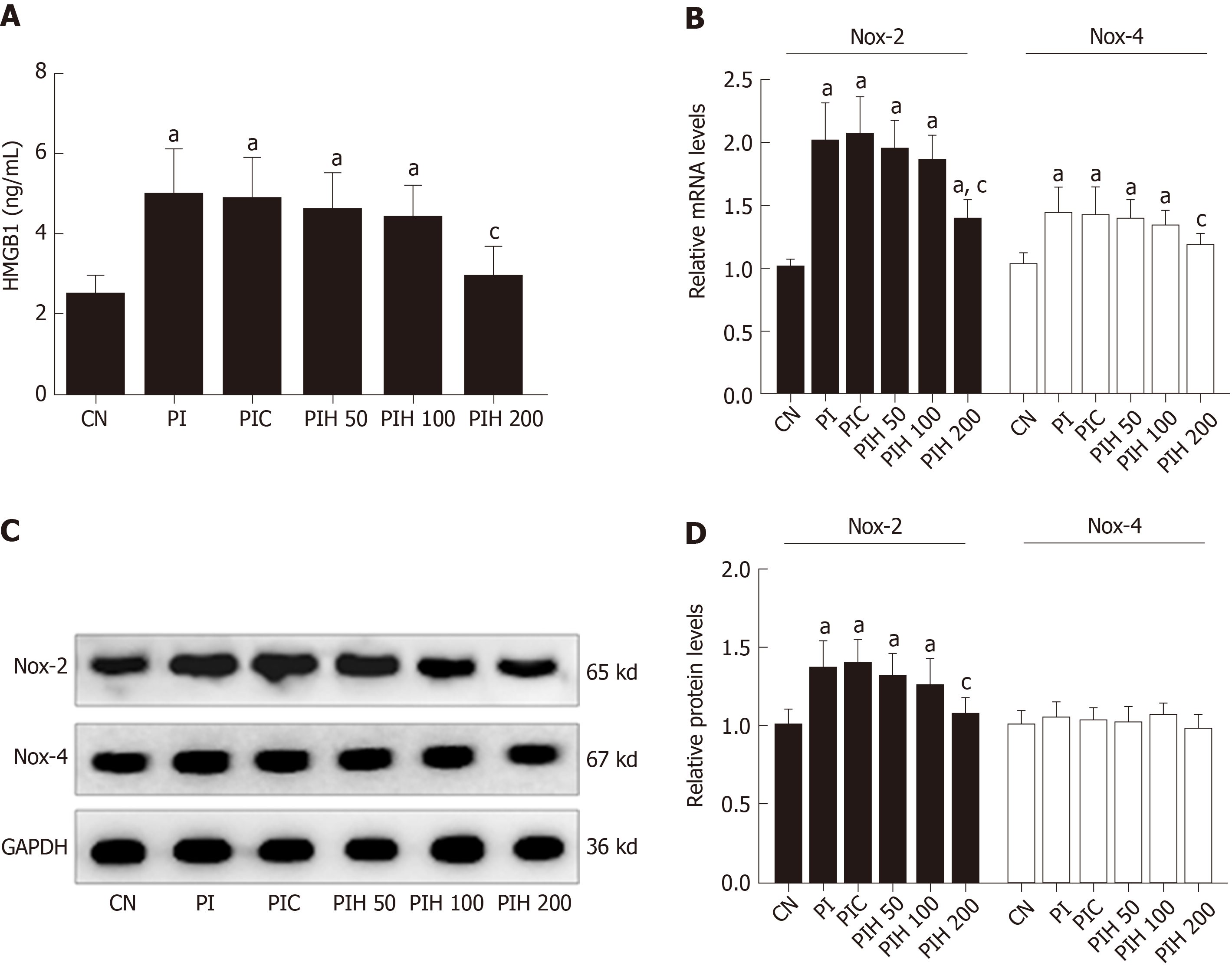
Figure 7 Effects of pancreatitis associated ascitic fluids intraperitoneal injection with or without anti-high mobility group box 1 neutralizing antibody on cardiac NOX expression in cerulein rats.
A: High mobility group box 1 in the serum; B: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-2 (NOX2) and NOX4 mRNA measurement by real-time polymerase chain reaction; C: Immunoblot of NOX2 and NOX4 protein expression from heart samples; D: Densitometry analysis of NOX2 and NOX4. Data indicate the mean ± standard deviation obtained from six animals in each group (A-B). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments (C-D). aP < 0.05 vs controls group; cP < 0.05 vs pancreatitis-associated ascitic fluid injection group. HMGB1: High mobility group box 1; NOX2: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-2; NOX4: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-4; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; APD: Abdominal paracentesis drainage.
- Citation: Wen Y, Sun HY, Tan Z, Liu RH, Huang SQ, Chen GY, Qi H, Tang LJ. Abdominal paracentesis drainage ameliorates myocardial injury in severe experimental pancreatitis rats through suppressing oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(1): 35-54
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i1/35.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.35