Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2019; 25(8): 923-940
Published online Feb 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i8.923
Published online Feb 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i8.923
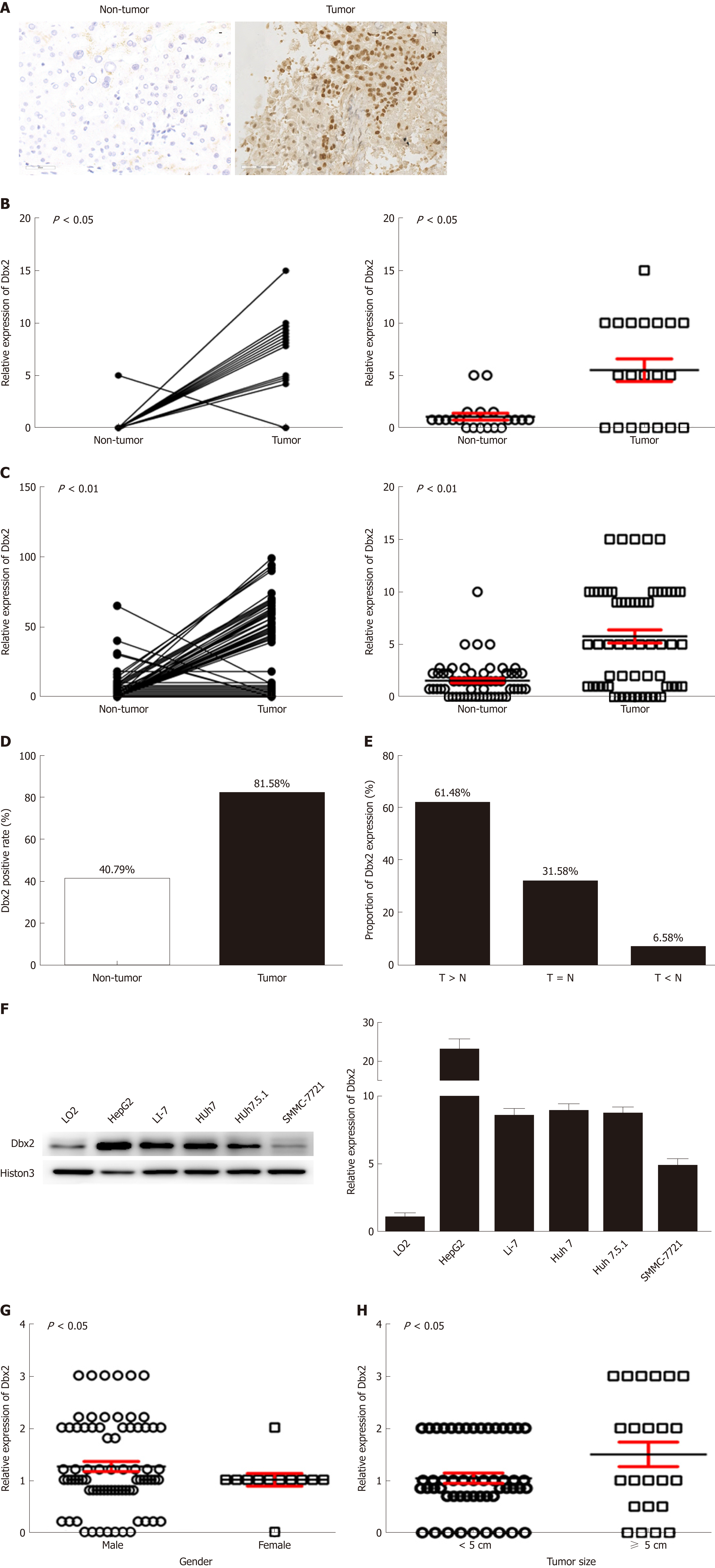
Figure 1 Developing brain homeobox 2 expression is frequently up-regulated in tumor tissues than in non-tumor tissues from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Positive developing brain homeobox 2 (Dbx2) expression in tumor tissues and negative Dbx2 expression in non-tumor tissues as revealed by immunohistochemistry (×400); B and C: Dbx2 expression was significantly upregulated in tumor tissues compared with their matched adjacent non-tumor tissues as revealed by immunohistochemistry; D and E: Relative Dbx2 expression in tumor tissues to paired non-tumor tissues; F: There was more Dbx2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells than in normal hepatic epithelial LO2 cells; G and H: Dbx2 expression was significantly related with gender and tumor size.
- Citation: Hu YT, Li BF, Zhang PJ, Wu D, Li YY, Li ZW, Shen L, Dong B, Gao J, Zhu X. Dbx2 exhibits a tumor-promoting function in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via regulating Shh-Gli1 signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(8): 923-940
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i8/923.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i8.923