Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2019; 25(7): 824-836
Published online Feb 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.824
Published online Feb 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.824
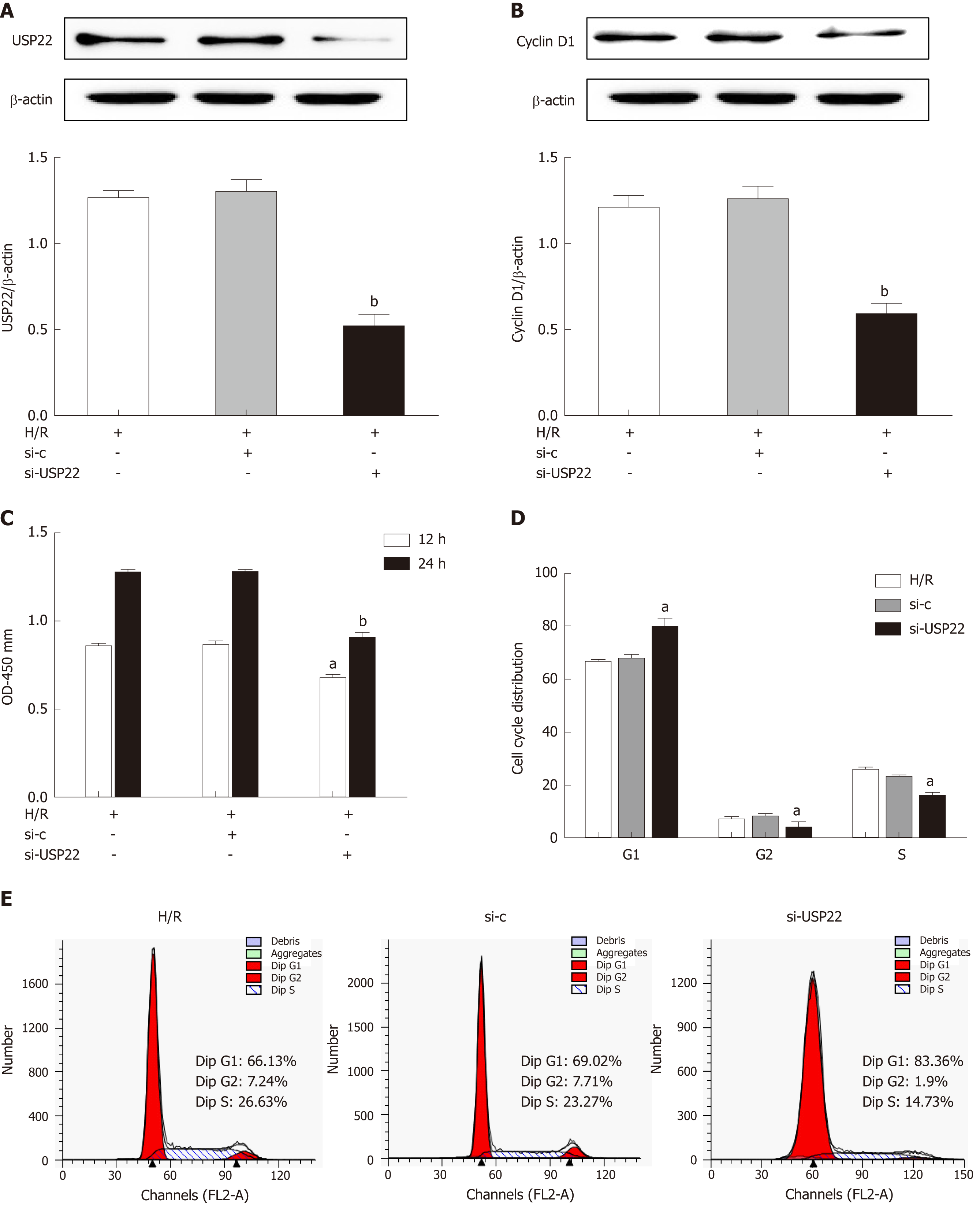
Figure 3 Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in IEC-6 cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation.
IEC-6 cells were transfected with USP22 siRNA or unspecific scrambled siRNA and then subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation or left untreated. A: Western blot analysis for USP22 and β-actin in ICE-6 cells transfected with USP22 siRNA and control siRNA (n = 3); B: Western blot analysis for Cyclin D1 and β-actin in ICE-6 cells transfected with USP22 siRNA and control siRNA (n = 3); C: CCK-8 was used to examine cell viability at the indicated time points (n = 6); D and E: FACSCalibur analysis of the percentages of cells in the G1, G2, and S phases at 24 h of reoxygenation after 6 h of hypoxia (n = 3). The results are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group. USP22: Ubiquitin-specific protease 22; CCK-8: Cell Counting Kit-8.
- Citation: Ji AL, Li T, Zu G, Feng DC, Li Y, Wang GZ, Yao JH, Tian XF. Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 enhances intestinal cell proliferation and tissue regeneration after intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(7): 824-836
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i7/824.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.824