Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2019; 25(7): 789-807
Published online Feb 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.789
Published online Feb 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.789
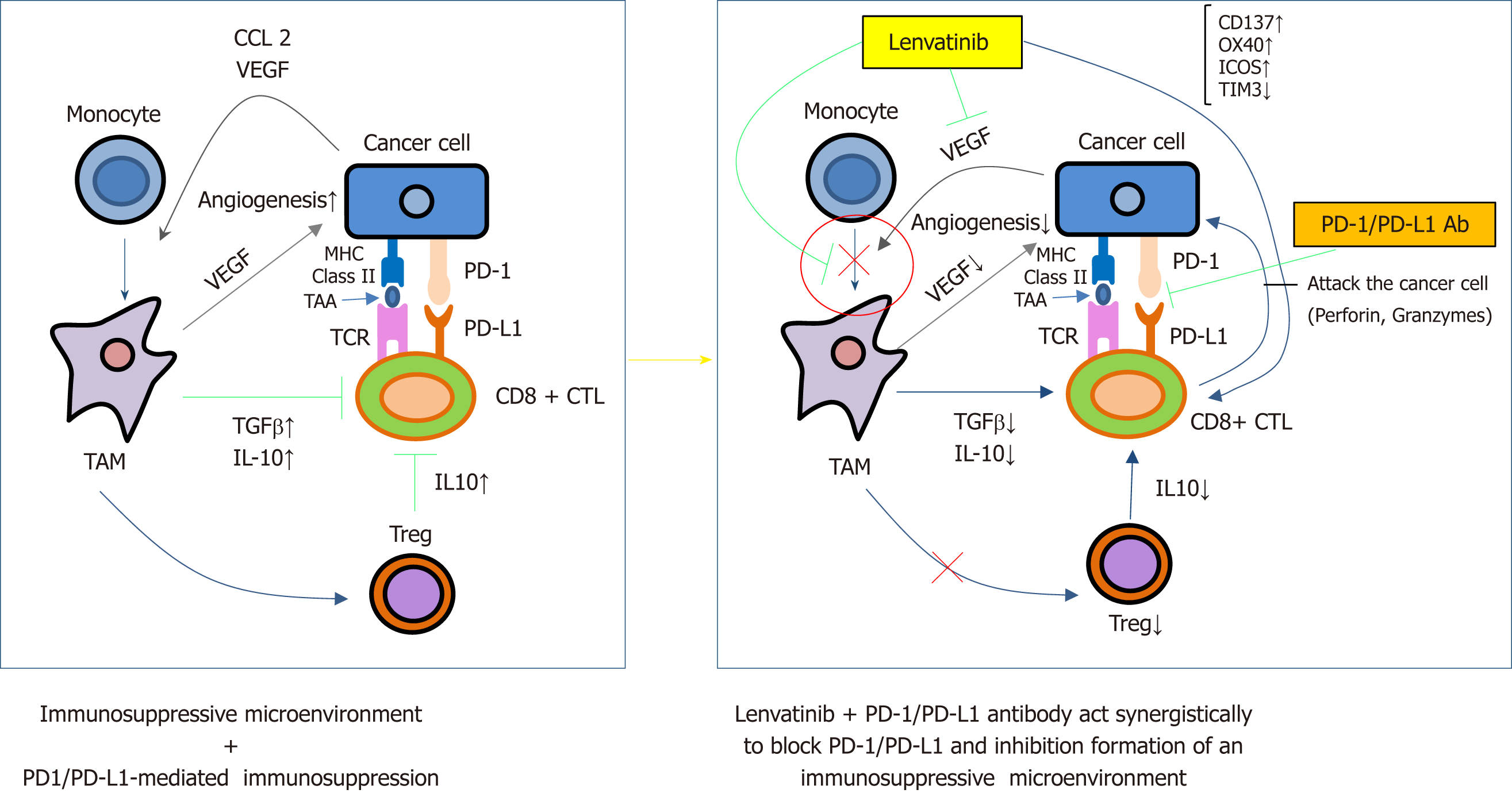
Figure 4 Mechanism underlying the synergistic effect of combination therapy on hepatocellular carcinoma with lenvatinib and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies[68].
Lenvatinib inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth through VEGFR1-R3 and FGFR1-R4 inhibition. Lenvatinib also inhibits VEGF-mediated tumor suppressive microenvironment, such as immunosuppressive cells (tumor associated macrophage, regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor T cells) or tumor suppressive cytokines (IL10 or TGF-β). Lenvatinib also suppress the co-inhibitory checkpoint inhibitor, TIM 3 and increase the co-stimulatory molecules, CD137, OX40 or ICOS. Finally, PD-1/PD-L1 Ab restores the exhausted T cell activity to kill the cancer cell. Therefore, synergistic effect is obtained by this combination.
- Citation: Kudo M. Targeted and immune therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: Predictions for 2019 and beyond. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(7): 789-807
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i7/789.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.789