Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2019; 25(6): 707-718
Published online Feb 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i6.707
Published online Feb 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i6.707
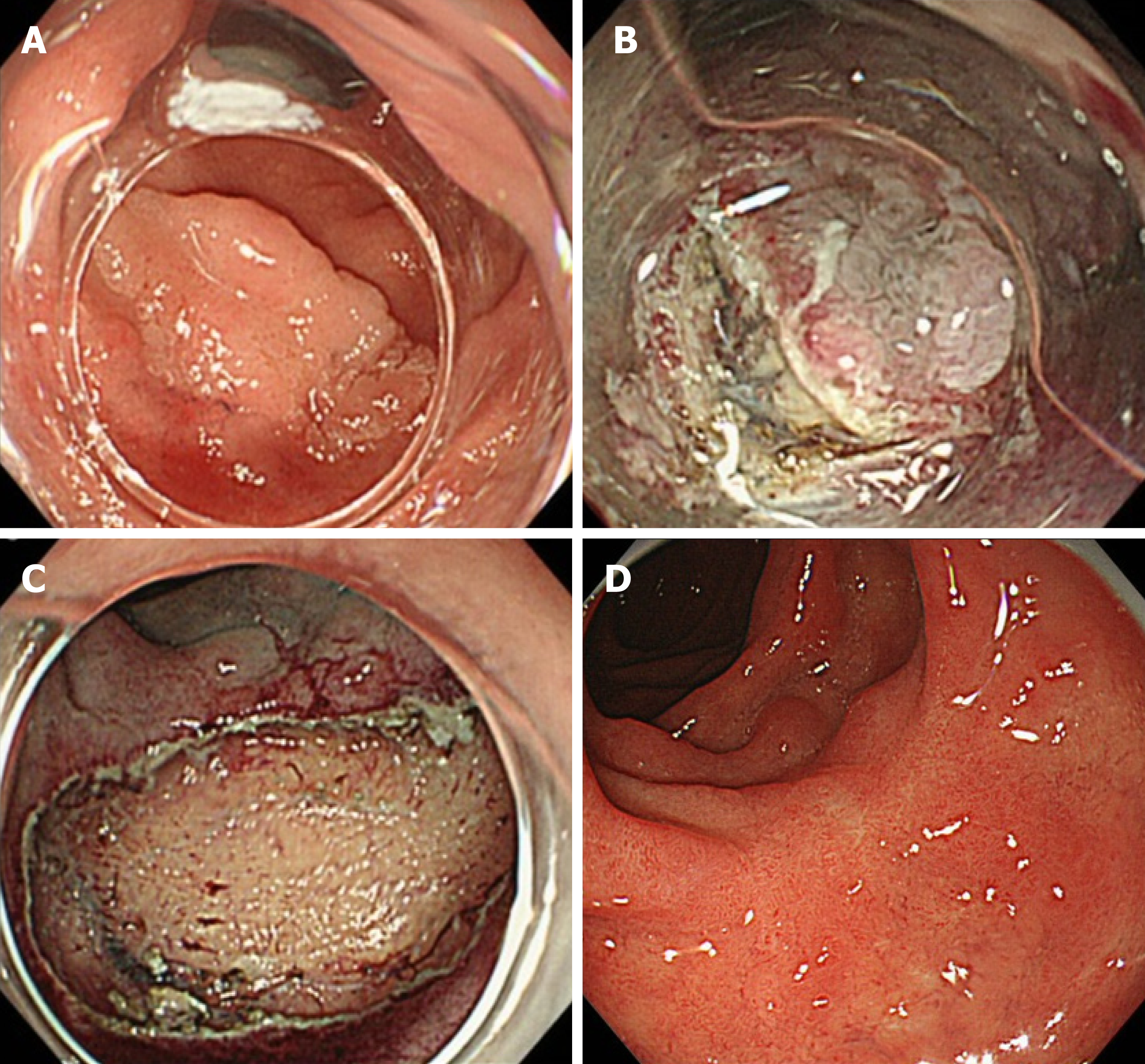
Figure 2 The endoscopic submucosal dissection method of superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors.
Type 0-IIa lesion, 25 mm × 25 mm, mucosal carcinoma, cut-end negative. A: Flat, elevated-type lesion was located in the second portion of the duodenum; B: Performing circumferential incision and submucosal dissection; C: Ulcer findings just after lesion removal. The lesion was resected en bloc, and there was no bleeding or perforation in the ulcer just after the procedure; D: After 2 mo of endoscopic submucosal dissection, the wound became a scar, and no residual tumor was found.
- Citation: Hara Y, Goda K, Dobashi A, Ohya TR, Kato M, Sumiyama K, Mitsuishi T, Hirooka S, Ikegami M, Tajiri H. Short- and long-term outcomes of endoscopically treated superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(6): 707-718
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i6/707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i6.707