Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2019; 25(44): 6495-6507
Published online Nov 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6495
Published online Nov 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6495
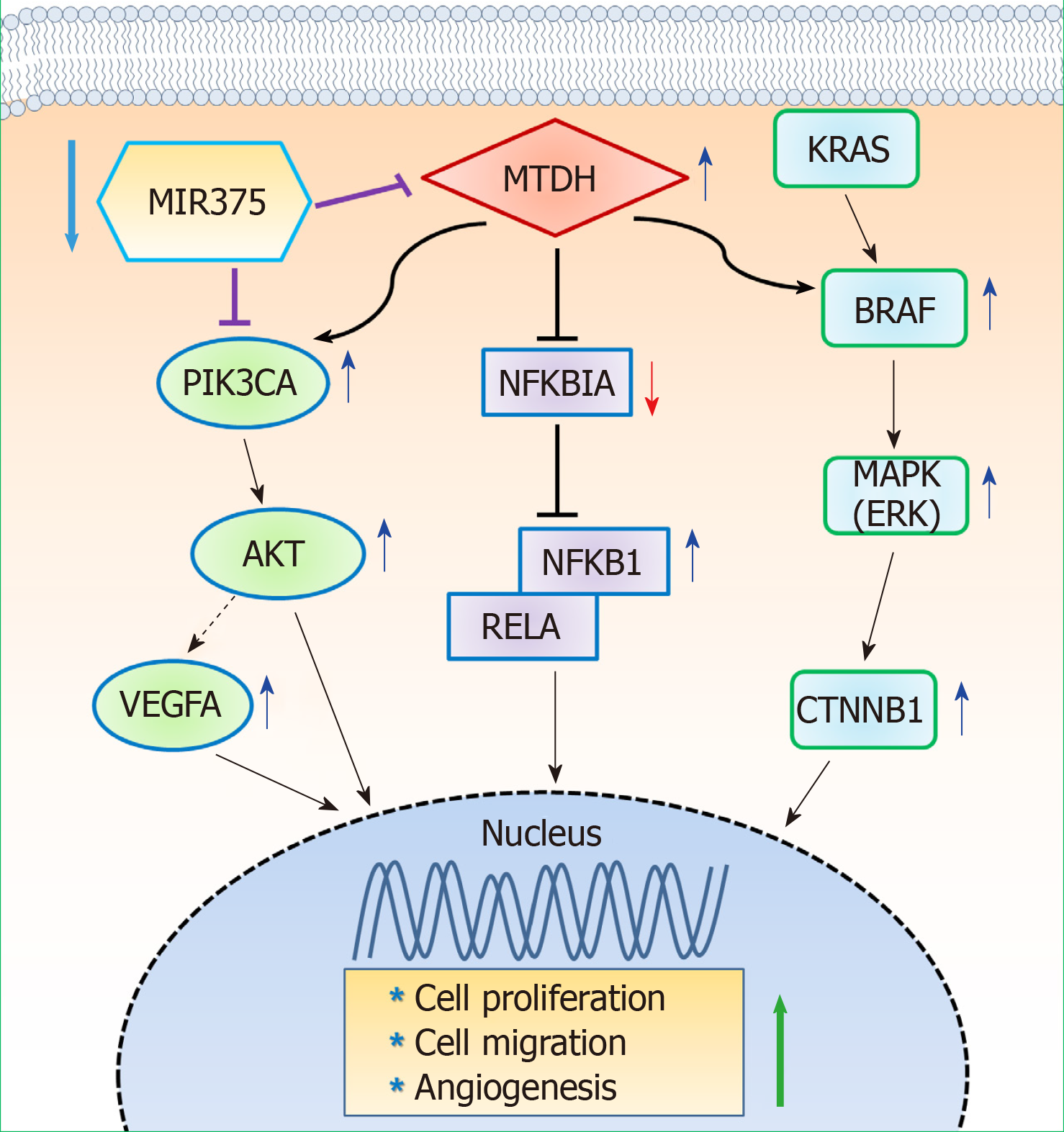
Figure 6 Diagrammatic representations of putative mechanisms of microRNA 375 in regulating metadherin-induced cell proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis in human colorectal cancer.
Decreased microRNA 375 (MIR375) expression in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells leads to upregulation of cellular metadherin (MTDH) levels. Subsequently, upregulated expression of MTDH promotes inhibition of NFKBIA and thus, NFKB1 and RELA expression is upregulated in CRC tissues and CRC cells. Upregulated MTDH expression level stimulates the BRAF-MAPK and PIK3CA-AKT signaling pathway. However, KRAS expression is unaltered by upregulation of MTDH. Consequently, downregulated MIR375 expression levels in CRC leads to upregulation of cell proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis. This simple hypothetical mechanism of MIR375-mediated upregulation of angiogenesis is based on the results of previous studies and our current study. MTDH: Metadherin; MIR375: MicroRNA 375; CRC: Colorectal cancer.
- Citation: Han SH, Mo JS, Park WC, Chae SC. Reduced microRNA 375 in colorectal cancer upregulates metadherin-mediated signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(44): 6495-6507
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i44/6495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6495