Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2019; 25(41): 6222-6237
Published online Nov 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6222
Published online Nov 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6222
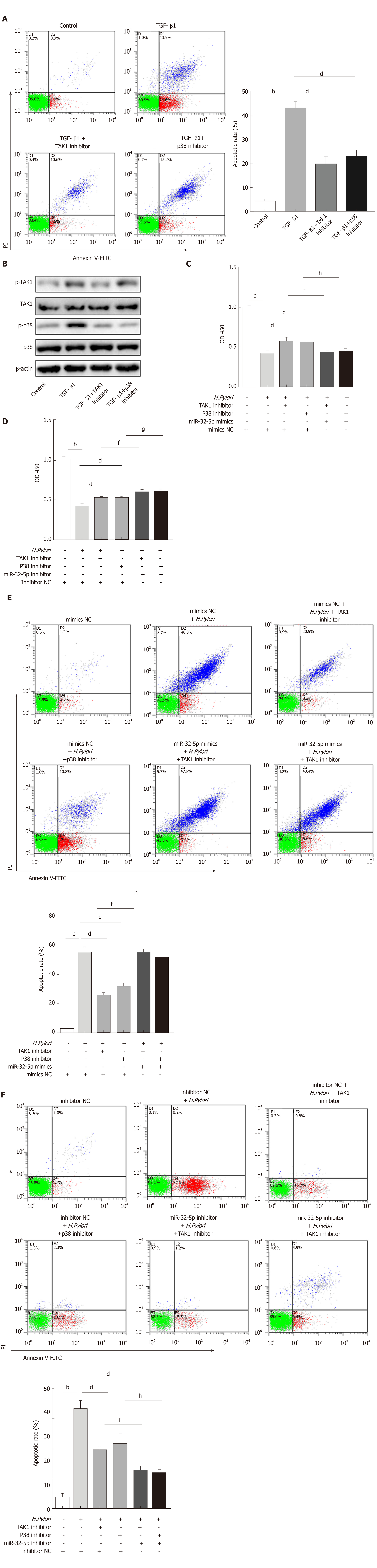
Figure 3 Transforming growth factor-β1/p38 participates in apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells infected by Helicobacter pylori.
A: Apoptosis detection in transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-treated intestinal epithelial cells in the presence of transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) inhibitor and p38 inhibitor; B: Protein levels of total TAK1, p38, phosphorylated TAK1, and phosphorylated p38 in TGF-β1-treated intestinal epithelial cells in the presence of TAK1 inhibitor and p38 inhibitor; C: Cell viability measurement in Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-infected intestinal epithelial cells with TAK1 inhibitor and p38 inhibitor treatment followed by transfection with miR-32-5p mimic; D: Cell viability measurement in H. pylori-infected intestinal epithelial cells with TAK1 inhibitor and p38 inhibitor treatment followed by transfection with miR-32-5p inhibitor; E: Apoptosis evaluation in H. pylori-infected intestinal epithelial cells with TAK1 inhibitor and p38 inhibitor treatment followed by transfection with miR-32-5p mimic; F: Apoptosis evaluation in H. pylori-infected intestinal epithelial cells with TAK1 inhibitor and p38 inhibitor treatment followed by transfection with miR-32-5p inhibitor. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.01, gP < 0.05, hP < 0.01. TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; TAK1: Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Feng J, Guo J, Wang JP, Chai BF. MiR-32-5p aggravates intestinal epithelial cell injury in pediatric enteritis induced by Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(41): 6222-6237
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i41/6222.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6222