Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
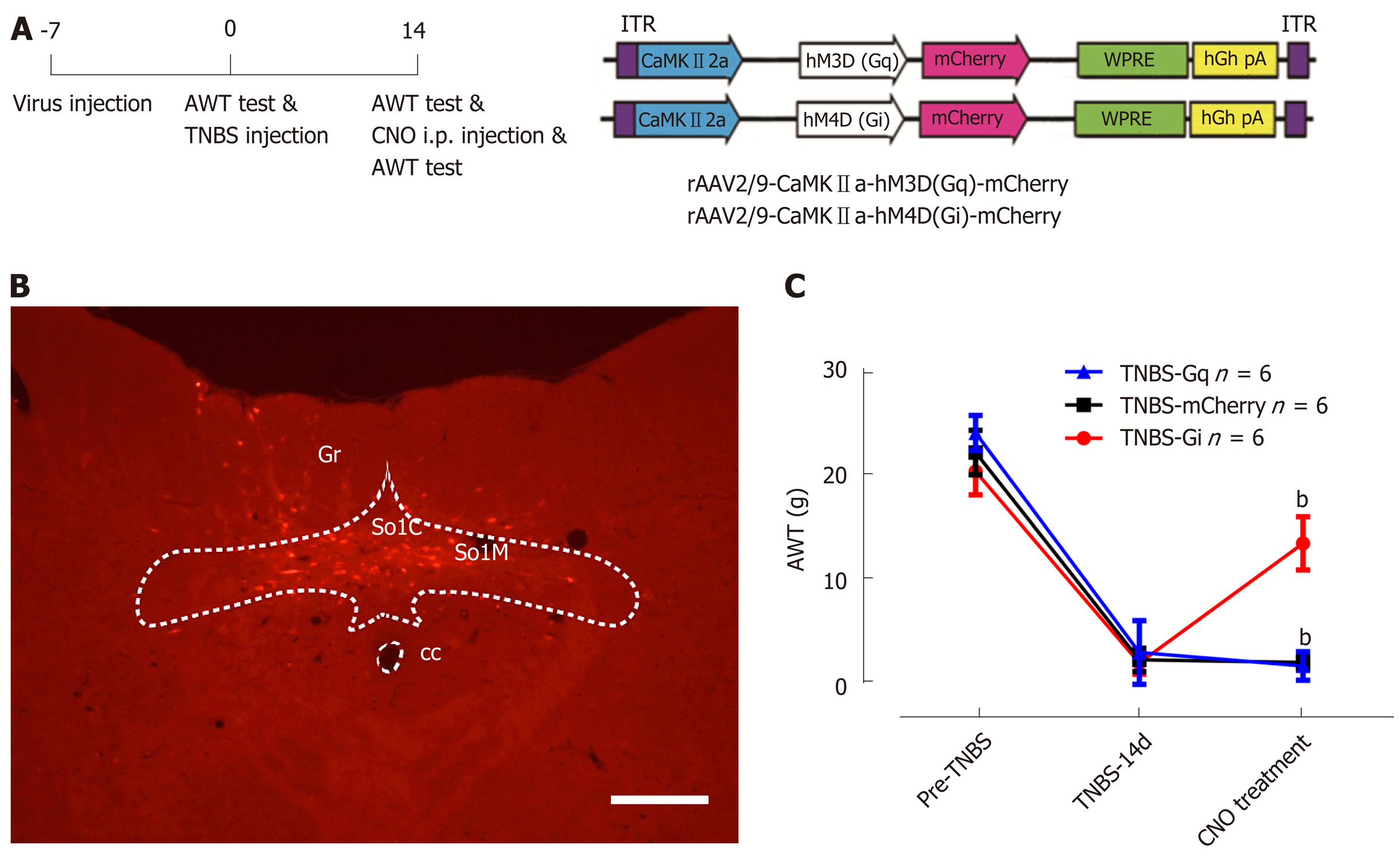
Figure 7 Inactivating excitatory neurons within the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius alleviates visceral hypersensitivity in rats with chronic pancreatitis.
A: The schematic diagram of behavioral experiment (left) and rAAV2/9-CaMKIIa-hM4Di/hM3Dq-mCherry construct (right); B: A representative image showing that the expression of hM4Di-mCherry was confined within the commissure and medial nuclei of the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS). Bar = 0.4 mm. C: Inhibiting caudal NTS excitatory neurons via i.p. clozapine-N-oxide injection significantly increases the abdominal withdraw threshold (AWT) in chronic pancreatitis rats, while activating these neurons does not influence the AWT. n = 6 rats in mCherry, Gq, and Gi groups, one-way ANOVA. bP < 0.01, Gi vs mCherry. AWT: Abdominal withdraw threshold; CC: Central canal; CNO: Clozapine-N-oxide; SolM: Nucleus of the solitary tract, medial part; SolC: Nucleus of the solitary tract, commissural part; Gr: Gracile nucleus; TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
- Citation: Bai Y, Chen YB, Qiu XT, Chen YB, Ma LT, Li YQ, Sun HK, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Chen T, Fan BY, Li H, Li YQ. Nucleus tractus solitarius mediates hyperalgesia induced by chronic pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077