Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
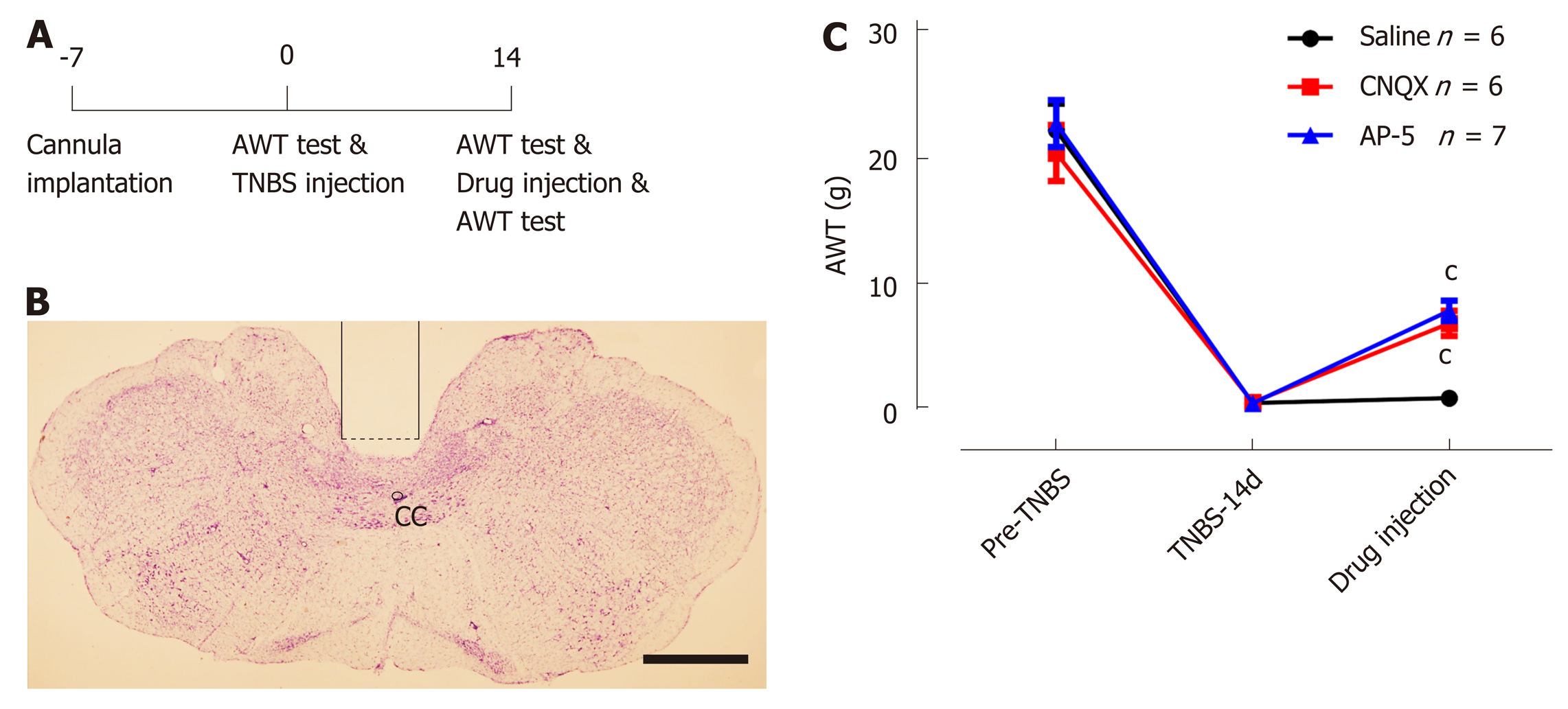
Figure 6 Administration of 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione and amino-5-phosphonopentaoic acid into the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius alleviates chronic pancreatitis induced visceral hypersensitivity.
A: Schematic diagram of behavioral test; B: A representative section showing the site of cannula implantation within the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius. Bar = 1 mm; C: Microinjection of 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) and amino-5-phosphonopentaoic acid (AP-5), instead of saline, increases the abdominal withdraw threshold in chronic pancreatitis rats on postoperative day 14. n = 6 rats in saline and CNQX-treated groups and 7 rats in AP5-treated group, one-way ANOVA, cP < 0.001, CNQX or AP5 groups vs saline group. AWT: Abdominal withdraw threshold; CC: Central canal; CNQX: 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione; AP-5: Amino-5-phosphonopentaoic acid; TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
- Citation: Bai Y, Chen YB, Qiu XT, Chen YB, Ma LT, Li YQ, Sun HK, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Chen T, Fan BY, Li H, Li YQ. Nucleus tractus solitarius mediates hyperalgesia induced by chronic pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077