Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
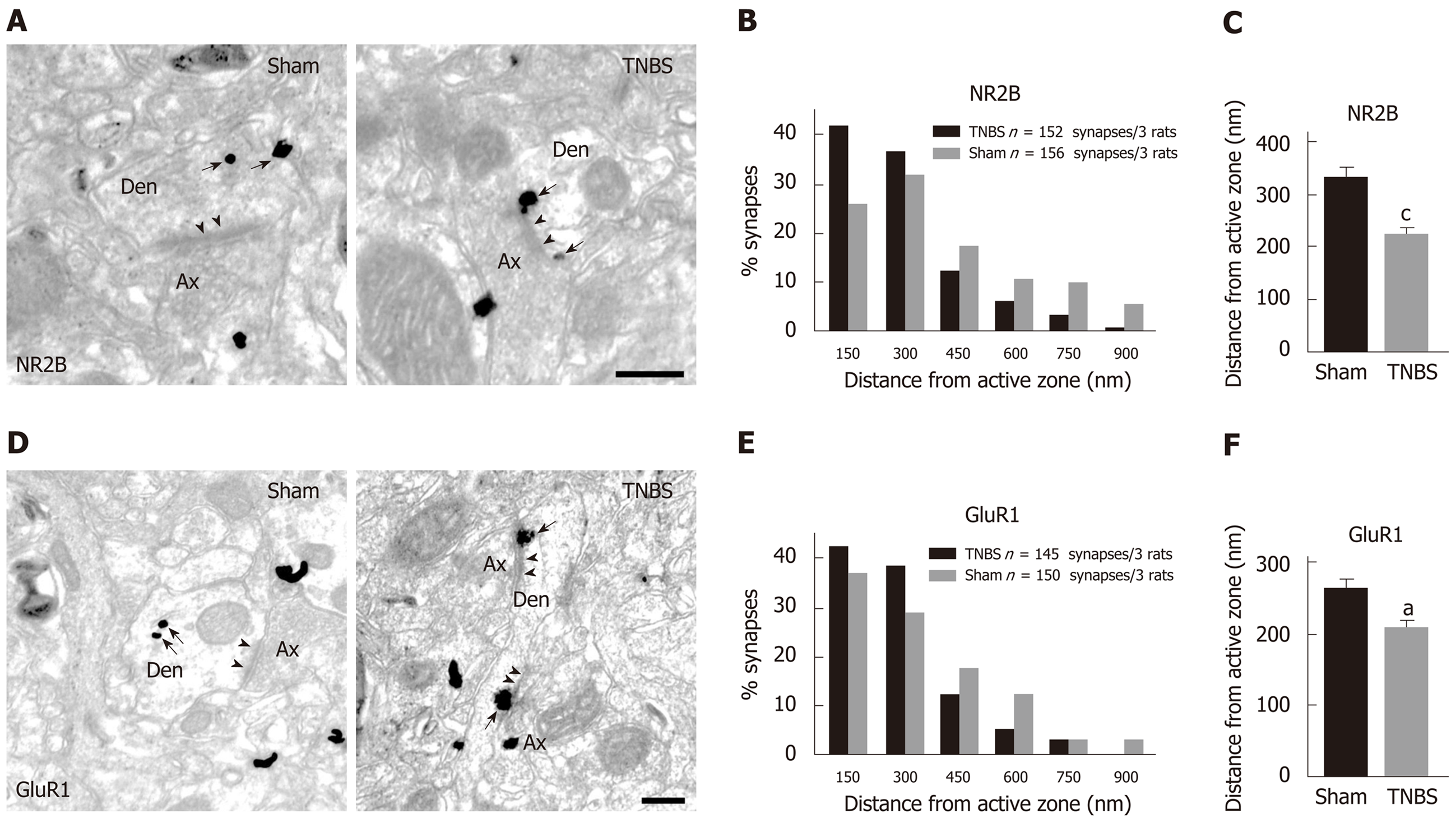
Figure 5 Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid treatment results in accumulation of postsynaptic N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor subtype 1 in the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius.
A: Representative electron microscopy images showing immune-gold particles labeled N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B (NR2B) distributed in an asymmetric synapse within the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of sham (left) and chronic pancreatitis (CP) (right) rats; B: Percentage of NR2B particles in 150 nm bins as a function of distance from the nearest edge of synapses; C: Averaged distances of NR2B from the edge of synapses of sham rats and CP rats; D: Representative electron microscopy images showing immune-gold particles labeled GluR1 distributed in an asymmetric synapse within caudal NTS of sham (left) and CP (right) rats; E: Percentage of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor subtype 1 (GluR1) particles in 150 nm bins as a function of distance from the nearest edge of synapses; F: Averaged distances of GluR1 from the edge of synapses of sham rats and CP rats. Bar = 250 nm in A and D. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001, TNBS vs sham. Ax: Axon; Den: Dendrite; GluR1: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor subtype 1; NR2B: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
- Citation: Bai Y, Chen YB, Qiu XT, Chen YB, Ma LT, Li YQ, Sun HK, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Chen T, Fan BY, Li H, Li YQ. Nucleus tractus solitarius mediates hyperalgesia induced by chronic pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077