Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
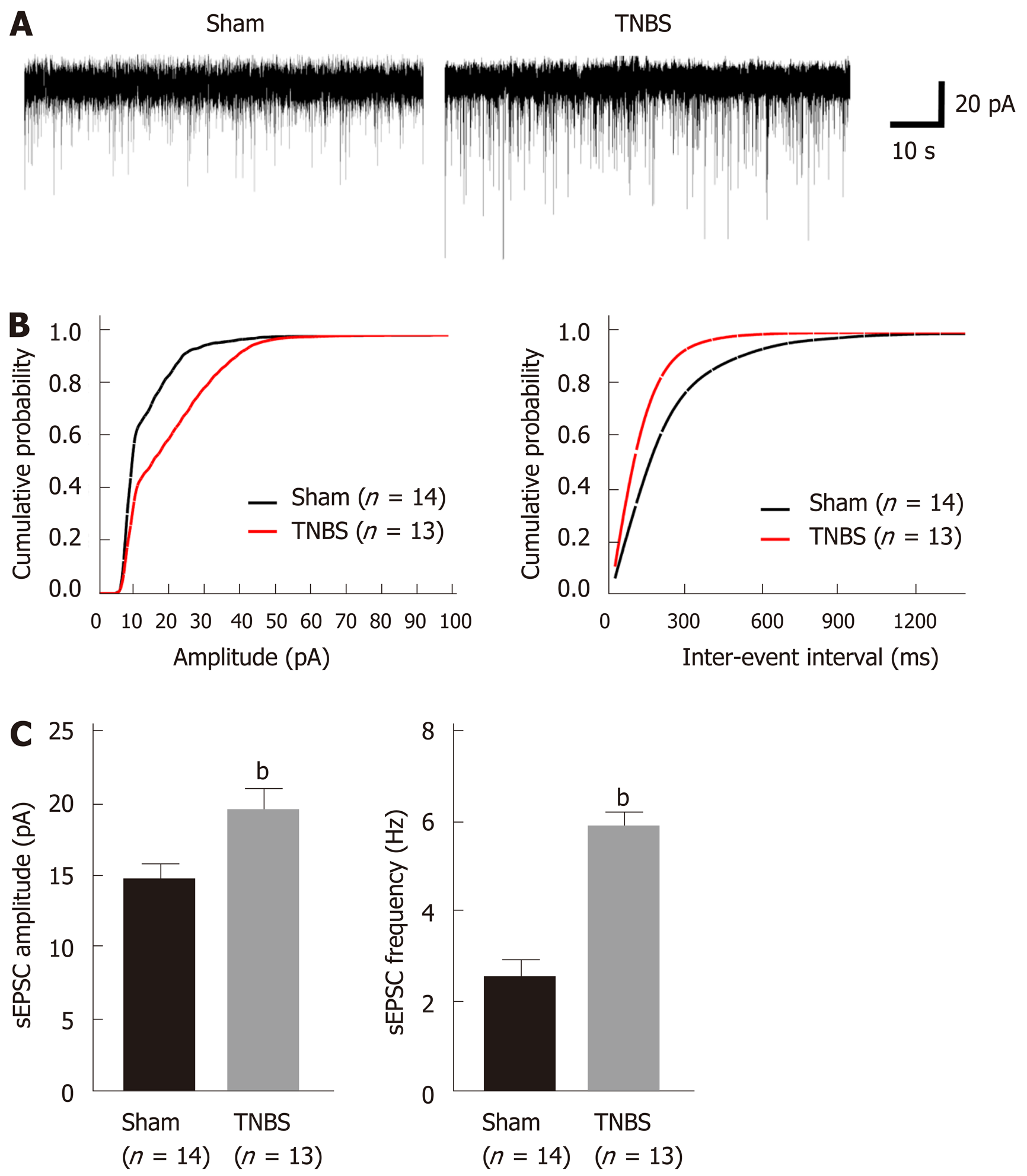
Figure 2 Rats with chronic pancreatitis have increased amplitude and frequency of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius.
A: Representative spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) recorded from a sham (left) rat and a trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-treated (right) rat holding at -60 mV; B: Cumulative amplitude (left) and inter-event interval (right) histograms of sEPSCs recorded from sham and chronic pancreatitis (CP) rats; C: Summary plots showing the frequency (left) and amplitude (right) of sEPSCs from sham and CP rats. Unpaired t-test, bP < 0.01, TNBS vs sham. sEPSC: Spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents; TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
- Citation: Bai Y, Chen YB, Qiu XT, Chen YB, Ma LT, Li YQ, Sun HK, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Chen T, Fan BY, Li H, Li YQ. Nucleus tractus solitarius mediates hyperalgesia induced by chronic pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077