Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
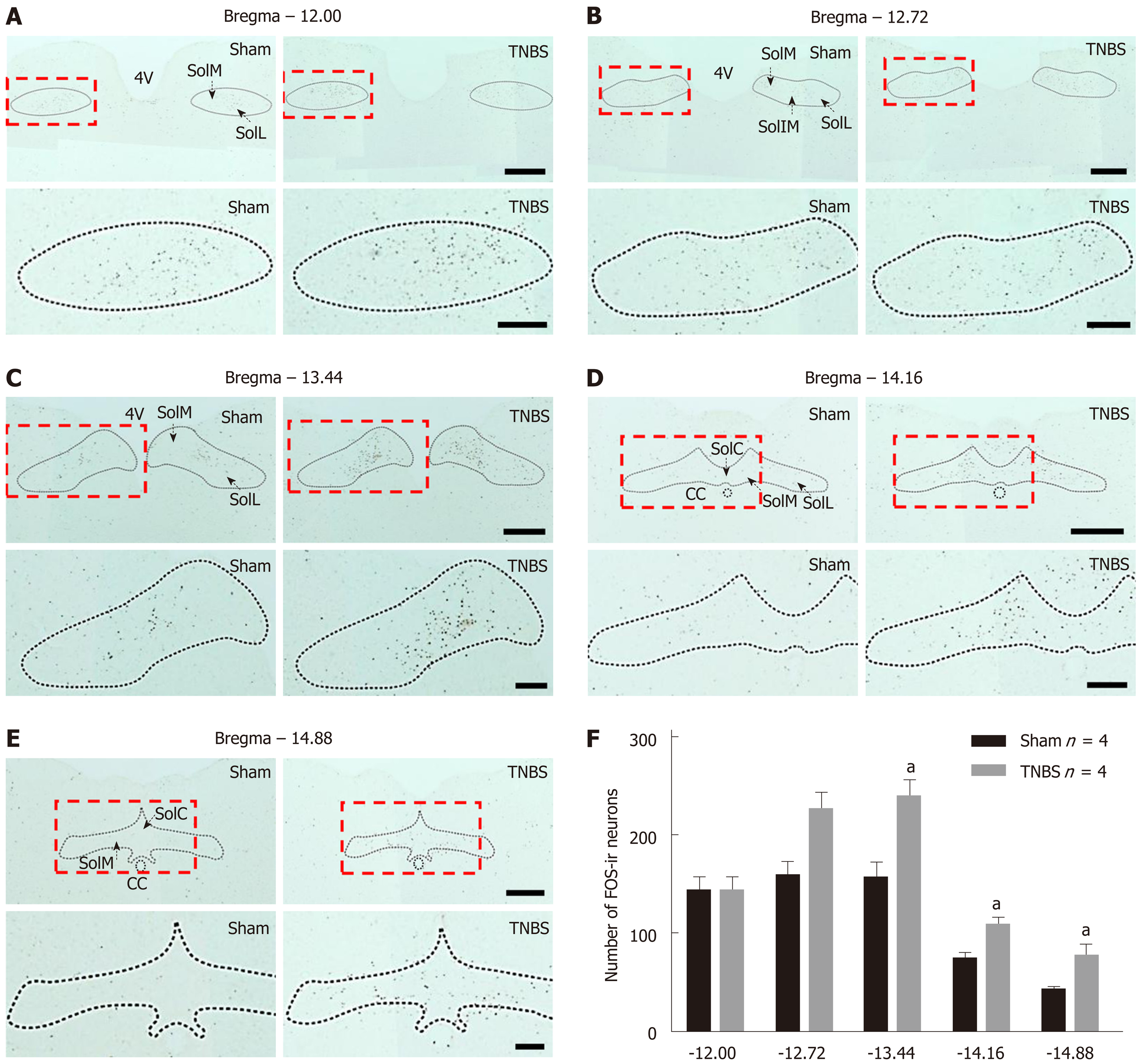
Figure 1 The number of Fos-expressing neurons is upregulated within the nucleus tractus solitarius in rats with chronic pancreatitis.
A-E: Immunochemical staining for Fos within different coronal sections of nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in sham (left) and chronic pancreatitis (right) rats. The rectangles in the top panels are further magnified in the bottom panels. Bars = 500 μm in top panels and 200 μm in bottom panels; F: Histogram showing the qualification of Fos-expressing neurons within different parts of NTS in saline and trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-treated rats. n = 4 rats per each group, unpaired t-test, aP < 0.05, TNBS vs sham. 4V: 4th ventricle; CC: Central canal; SolIM: Nucleus of the solitary tract, intermedial part; SolM: Nucleus of the solitary tract, medial part; SolL: Nucleus of the solitary tract, lateral part; SolC: Nucleus of the solitary tract, commissural part; TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
- Citation: Bai Y, Chen YB, Qiu XT, Chen YB, Ma LT, Li YQ, Sun HK, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Chen T, Fan BY, Li H, Li YQ. Nucleus tractus solitarius mediates hyperalgesia induced by chronic pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077