Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6063-6076
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6063
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6063
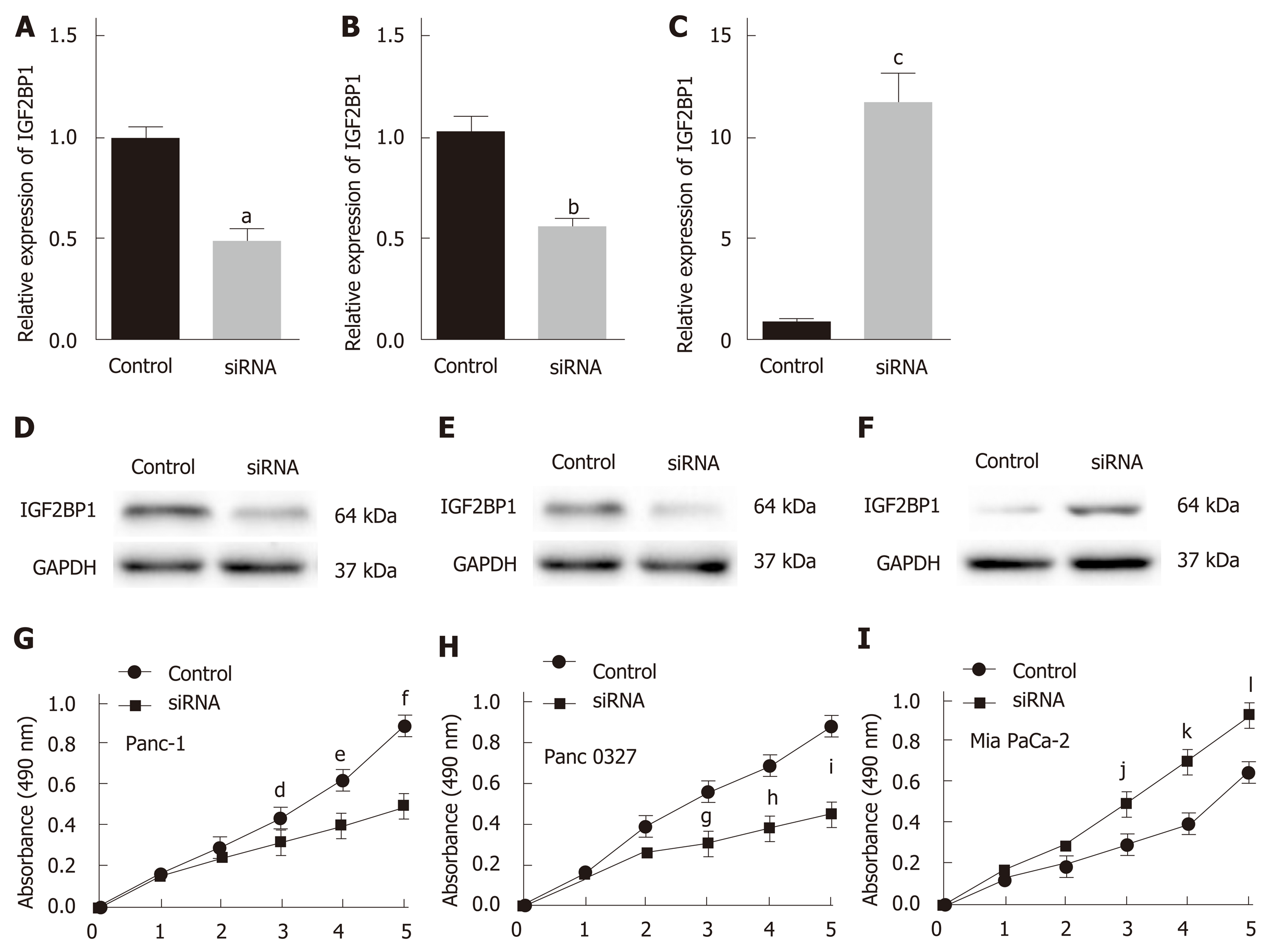
Figure 2 Knockdown of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation in vitro.
A-C: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) levels were determined by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis 48 h after transfection; D-F: IGF2BP1 levels were determined by Western blot analysis 48 h after transfection; G-I: CCK-8 assays were performed to compare the proliferation of IGF2BP1 knockdown or overexpressing cells vs the control cells. GAPDH served as the loading control. All data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments at least and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. aP < 0.05 vs siRNA group; bP < 0.05 vs normal group; cP < 0.01 vs IGF2BP1-OE group; dP < 0.05 vs siRNA at day 3; eP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 4; fP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 5; gP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 3; hP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 4; iP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 5; jP < 0.05 vs siRNA at day 3; kP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 4; lP < 0.01 vs siRNA at day 5. IGF2BP1: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1.
- Citation: Wan BS, Cheng M, Zhang L. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 promotes cell proliferation via activation of AKT and is directly targeted by microRNA-494 in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6063-6076
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6063.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6063