Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6063-6076
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6063
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6063
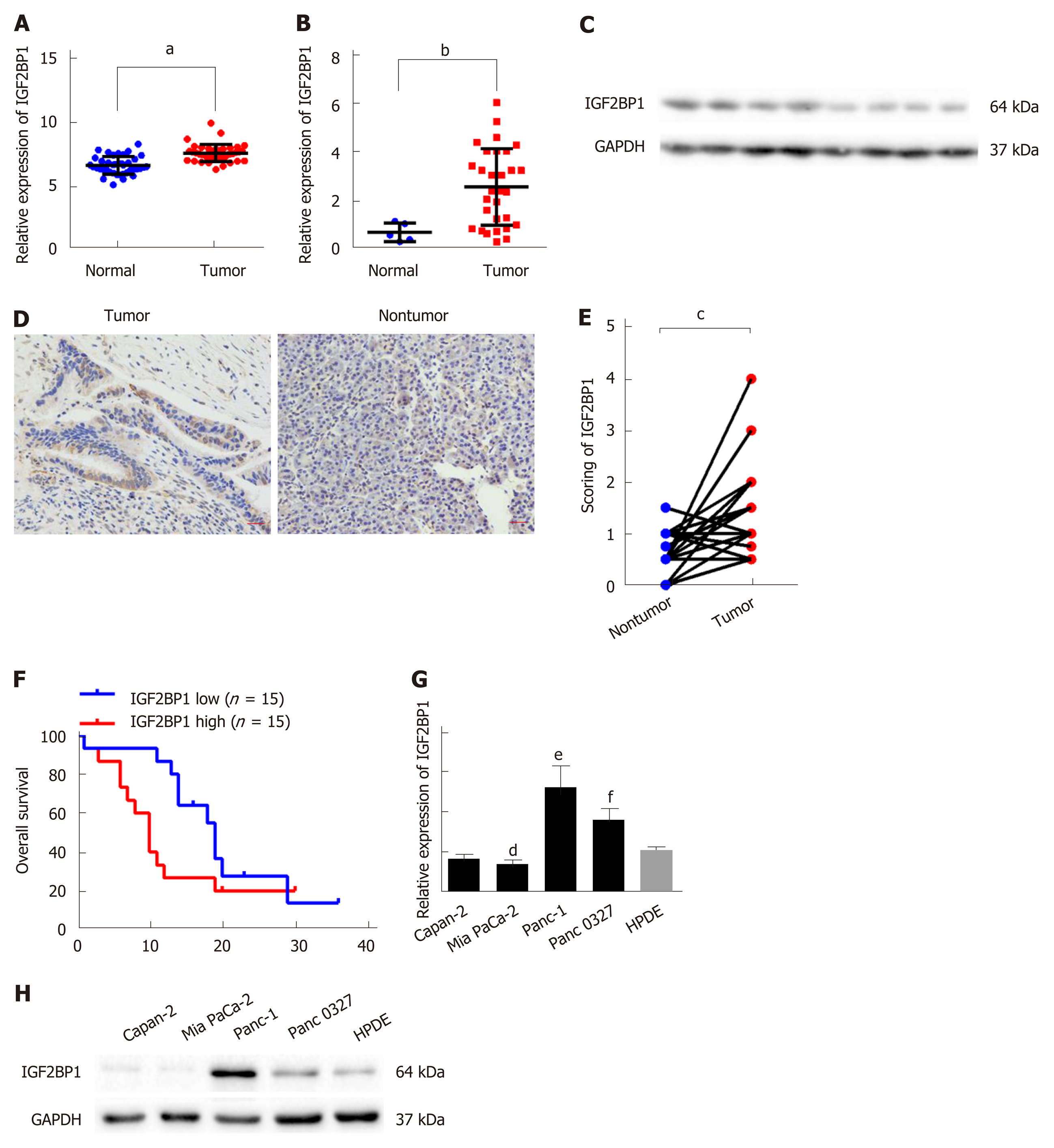
Figure 1 Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 overexpression correlates with a poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer.
A: The mRNA level of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) was analyzed in the GSE15471 pancreatic cancer dataset; B: The mRNA level of IGF2BP1 was determined by reverse transcription real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in 30 cancerous tissues and five normal pancreatic tissues from patients at The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University. GAPDH served as the internal reference; C: The protein level of IGF2BP1 was determined by immunoblotting in five cancerous tissues and three normal pancreatic tissues; D: Representative images of IGF2BP1 in pancreatic cancer tissues and their corresponding nontumor tissues by immunohistochemistry. Scale bar = 25 μm (red line); E: Quantitative analysis of the IGF2BP1 expression score in pancreatic cancer tissues and adjacent nontumor tissues; F: Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival of patients with pancreatic cancer according to the expression level of IGF2BP1; G-H: The mRNA and protein expression levels of IGF2BP1 in four pancreatic cancer cell lines compared with the expression levels in immortalized human pancreatic ductal epithelial cells (HPDE). GAPDH served as the loading control. All data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments at least and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. aP < 0.001 vs normal group; bP < 0.05 vs normal group; cP < 0.001 vs nontumor group; dP < 0.05 vs HPDE, eP < 0.05 vs HPDE, fP < 0.05 vs HPDE. HPDE: Human pancreatic ductal epithelial cells; IGF2BP1: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1.
- Citation: Wan BS, Cheng M, Zhang L. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 promotes cell proliferation via activation of AKT and is directly targeted by microRNA-494 in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6063-6076
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6063.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6063