Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2019; 25(39): 5961-5972
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5961
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5961
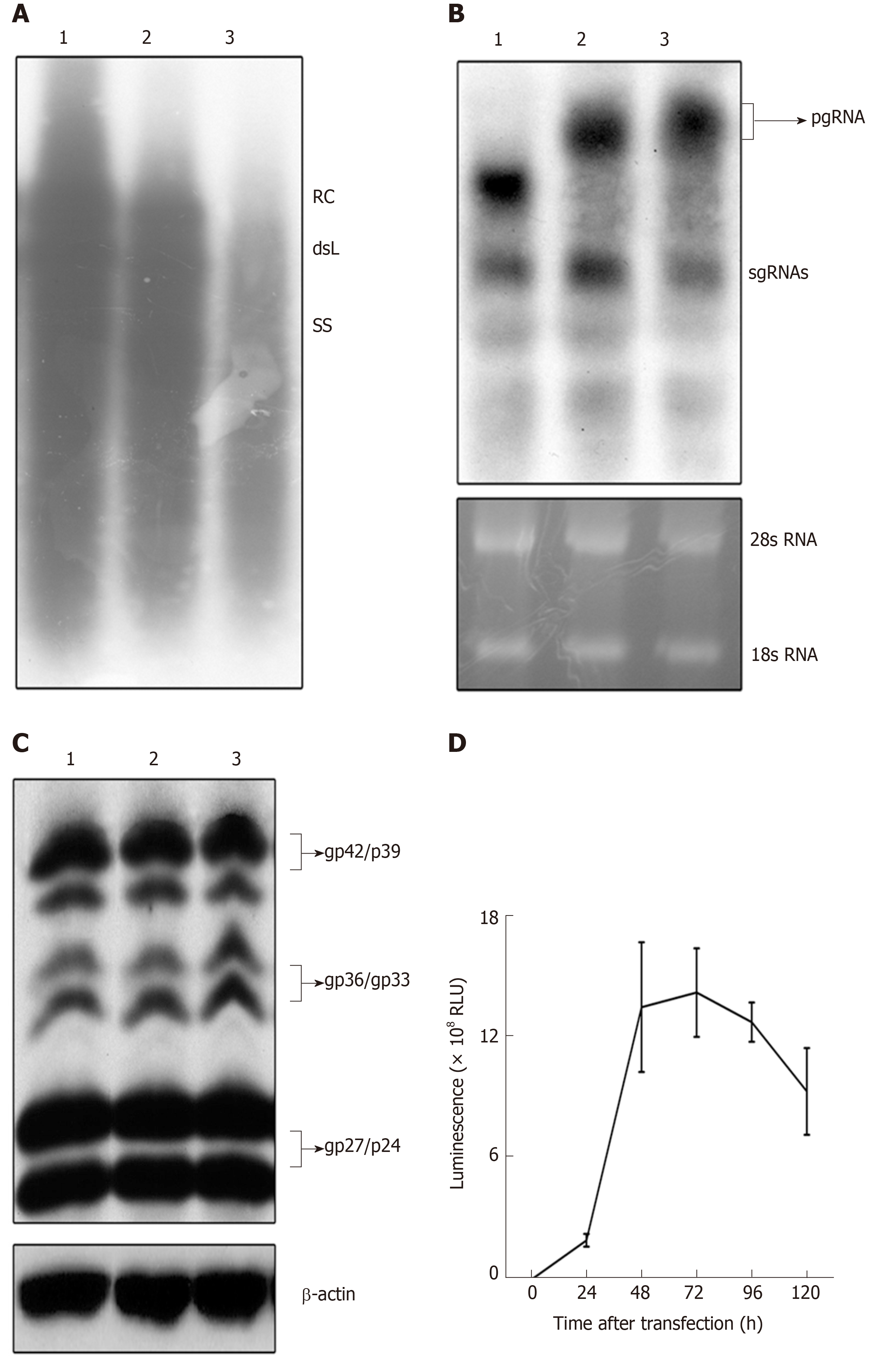
Figure 2 Detection of expression and replication of the recombinant hepatitis B virus vectors.
HepG2 cells were transfected with pCH-3093 (1), pCH-BsdR (2), and pCH-sNLuc (3). A: Replication efficiency of HBV vectors. Cytoplasmic HBV DNA was detected at 4 d post-transfection, and replicative intermediates were monitored by Southern blot using a 32P-labeled HBV probe. The positions of relaxed circular and double-stranded linear DNA are indicated; B: Detection of the RNA transcription of HBV vectors. Total intracellular RNA was analyzed by Northern blot with a 32P-labeled HBV-specific probe. The positions of the pregenomic RNA and subgenomic RNAs are indicated, and 28S and 18S rRNA bands are shown as loading controls; C: Detection of envelope protein expression of HBV vectors. Western blot analysis was performed using a 4/7B HBsAg antibody. The bands correspond to the L protein (gp42/p39), M protein (gp36/gp33), and S protein (gp27/p24), and β-actin was used as a loading control; D: The dynamic luciferase activity of pCH-sNLuc. The vector pCH-sNLuc was transiently transfected into HepG2 cells, and luciferase expression in the supernatant was detected at the indicated time points (24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 h). HBV: Hepatitis B virus; RLU: Relative light unit; dsL: Double-stranded linear; RC: Relaxed circular; pgRNA: Pregenomic RNA; sgRNAs: Subgenomic RNAs.
- Citation: Ruan J, Ping CY, Sun S, Cheng X, Han PY, Zhang YG, Sun DX. Construction of a replication-competent hepatitis B virus vector carrying secreted luciferase transgene and establishment of new hepatitis B virus replication and expression cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(39): 5961-5972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i39/5961.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5961