Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2019; 25(39): 5936-5952
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5936
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5936
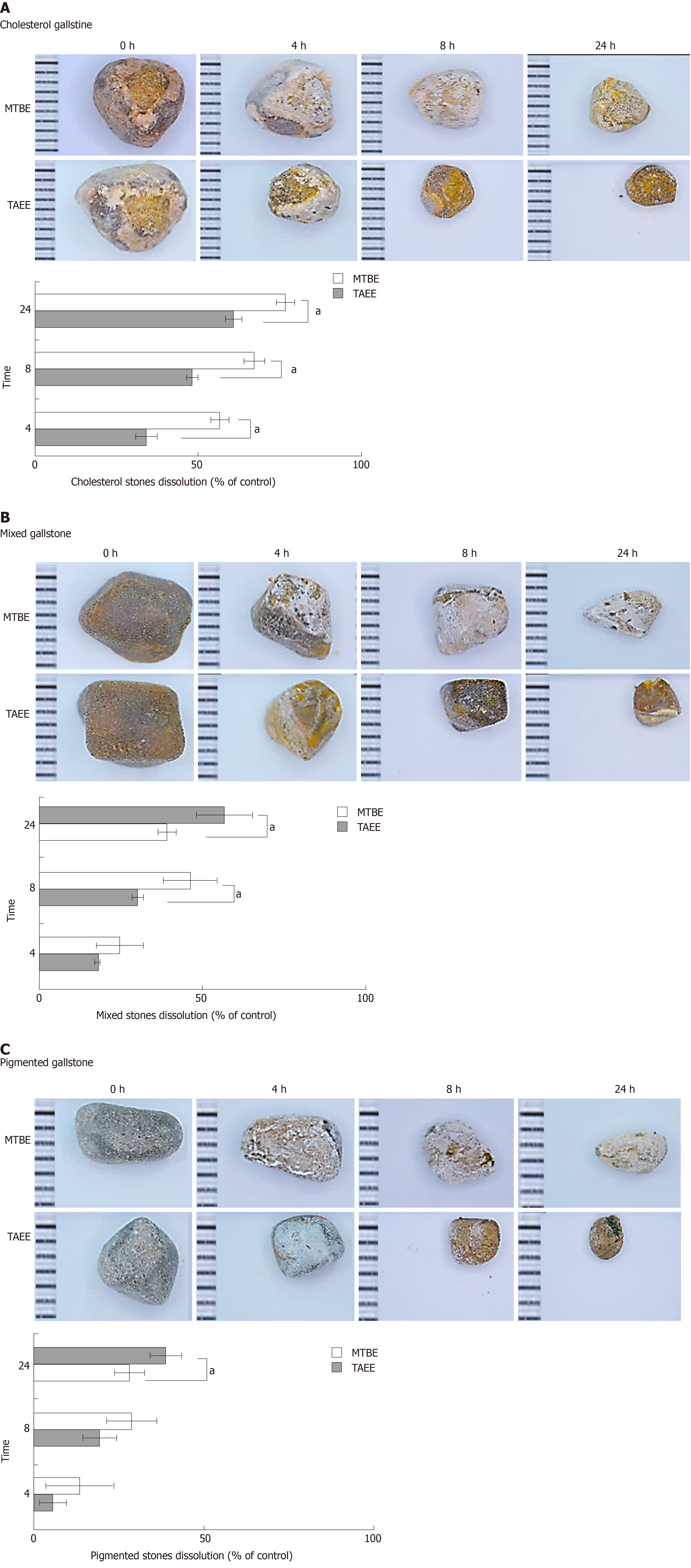
Figure 3 In vitro validation of gallstone dissolubility of each solvent.
A: Dissolubility exerted by each solvent for the cholesterol gallstones. Representative pictures of the residual cholesterol gallstones at 0 h, 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h after treatment (Left). Time-response graph demonstrating the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones. Tert-amyl ethyl ether (TAEE) dissolved the cholesterol gallstones significantly better than methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE) after 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h (P < 0.05) (Right); B: Dissolubility exerted by each solvent for the mixed gallstones. Representative pictures of the residual mixed gallstones at 0 h, 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h after treatment (Left). Time-response graph demonstrating the dissolution of mixed gallstones. TAEE dissolved the mixed gallstones significantly better than MTBE after 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h (P < 0.05) (Right); C: Dissolubility exerted by each solvent for the pigmented gallstones. Representative pictures of the residual pigmented gallstones at 0 h, 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h after treatment (Left). Time-response graph demonstrating the dissolution of pigmented gallstones. TAEE dissolved the pigmented gallstones significantly better than MTBE after 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h (P < 0.05) (Right). Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 between MTBE and TAEE. MTBE: Methyl tert-butyl ether; TAEE: Tert-amyl ethyl ether.
- Citation: You DD, Cho SJ, Kim OH, Song JS, Hwang KS, Lee SC, Kim KH, Choi HJ, Hong HE, Seo H, Hong TH, Park JH, Lee TY, Ahn J, Jung JK, Jung KY, Kim SJ. Superior gallstone dissolubility and safety of tert-amyl ethyl ether over methyl-tertiary butyl ether. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(39): 5936-5952
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i39/5936.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5936