Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2019; 25(38): 5850-5861
Published online Oct 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i38.5850
Published online Oct 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i38.5850
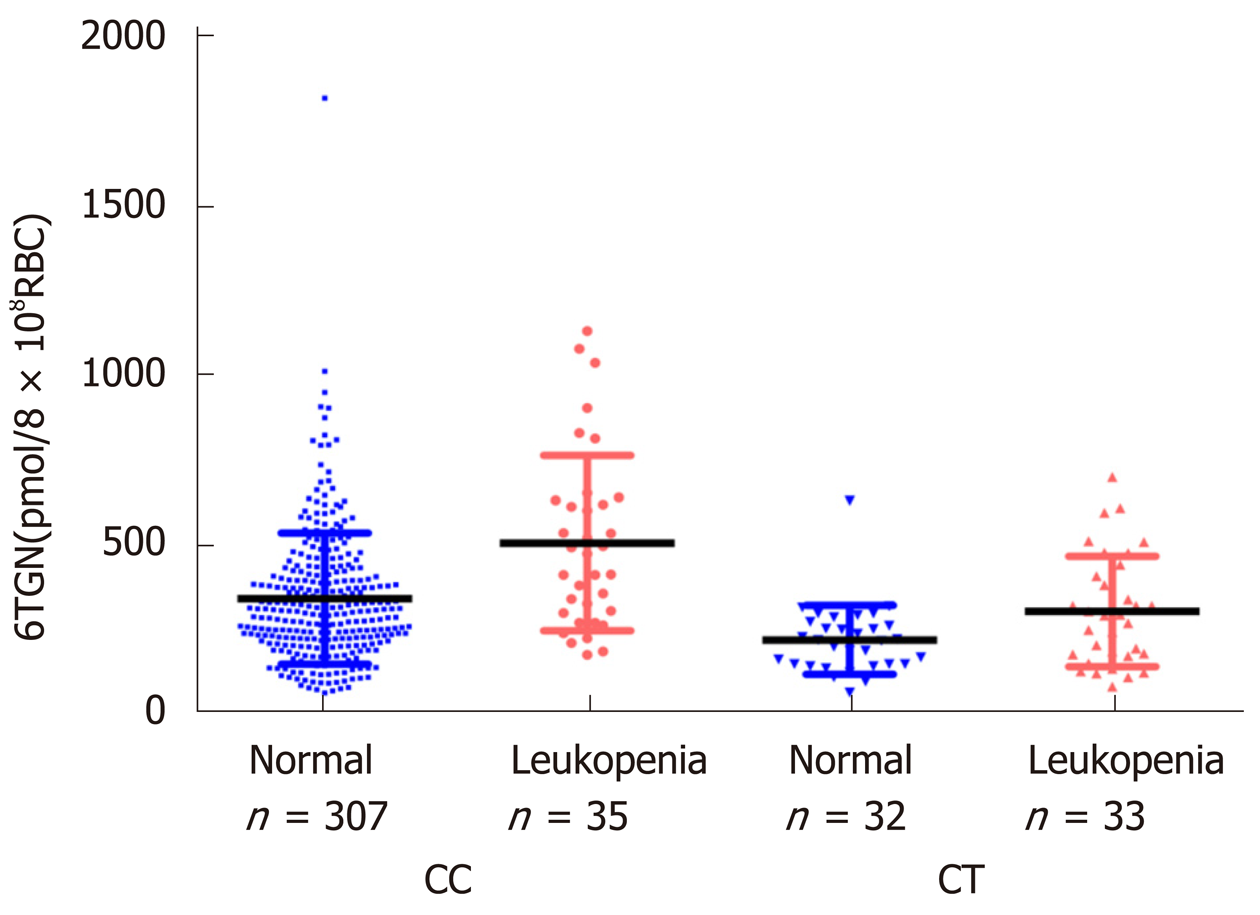
Figure 2 Relationship between thiopurine-induced leukopenia and 6-thioguanine nucleotide concentrations in different nucleoside diphosphate-linked moiety X-type motif 15 R139C genotypes.
In the CC group (n = 342), the median 6-thioguanine nucleotide (6TGN) concentration in patients who developed leukopenia was significantly higher than that in patients who did not [bP < 0.01, 474.8 (174.2-1133.6) pmol/8 × 108 red blood cells (RBC) vs 306.0 (62.2-1823.0) pmol/8 × 108 RBC]. In the CT group (n = 65), 6TGN level was also significantly higher in patients who developed leukopenia [aP < 0.05, 291.7 (80.6-701.5) vs 217.6 (62.9-631.0) pmol/8 × 108 RBC]. 6TGN: 6-thioguanine nucleotide; RBC: Red blood cells.
- Citation: Zhu X, Chao K, Li M, Xie W, Zheng H, Zhang JX, Hu PJ, Huang M, Gao X, Wang XD. Nucleoside diphosphate-linked moiety X-type motif 15 R139C genotypes impact 6-thioguanine nucleotide cut-off levels to predict thiopurine-induced leukopenia in Crohn’s disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(38): 5850-5861
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i38/5850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i38.5850