Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2019; 25(35): 5283-5299
Published online Sep 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i35.5283
Published online Sep 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i35.5283
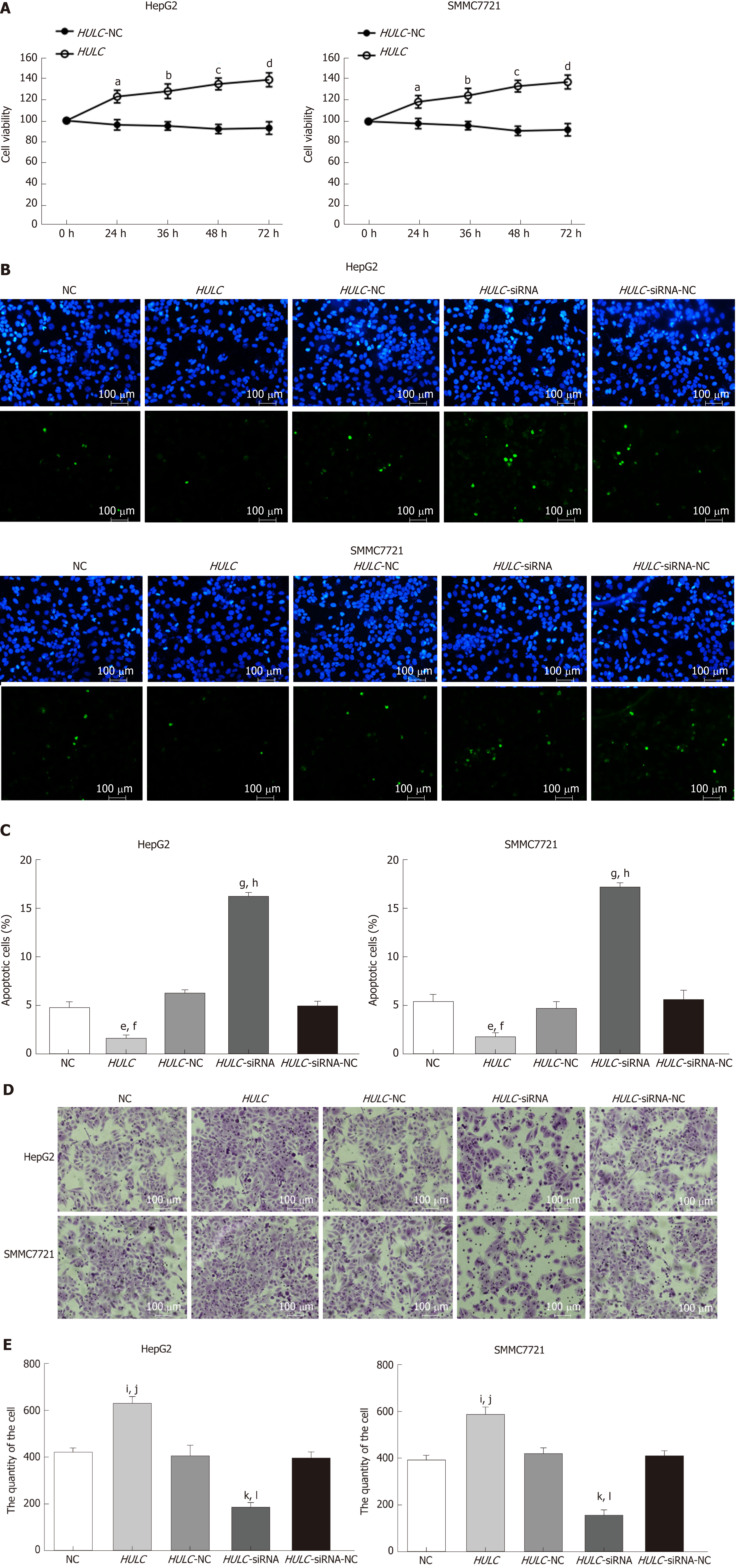
Figure 4 Long non-coding RNA highly up-regulated in liver cancer induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion and inhibits apoptosis in vitro.
A: Proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells transfected with HULC inhibitors or plasmids causing HULC overexpression; B: Apoptotic pictures of HCC cells (×100). The blue fluorescence is DAPI nuclear staining and green fluorescence is the apoptotic cell. The index of apoptosis is the number of apoptotic cells/total number of visual field × 100%; C: Column chart of index of apoptosis in different groups; D: Effect of HULC on invasion of HCC cells evaluated bTranswell assay (×100); E: Column chart of number of invasive HCC cells in different groups. Error bars stand for the mean ± SD of at least triplicate experiments. aP < 0.05 vs HULC-NC 24 h group; bP < 0.05 vs HULC-NC 36 h group; cP < 0.05 vs HULC-NC 48 h group; dP < 0.05 vs HULC-NC 72 h group; eP < 0.05 vs NC group; fP < 0.05 vs HULC-NC group; gP < 0.01 vs NC group; hP < 0.01 vs HULC-siRNA-NC group; iP < 0.05 vs NC group; jP < 0.05 vs HULC-NC group; kP < 0.05 vs NC group; lP < 0.05 vs HULC-siRNA-NC group. HULC: Highly upregulated in liver cancer; NC: Normal control group; HULC: HULC over-expression plasmid group; HULC-NC: HULC over-expression normal control plasmid group; HULC-siRNA: HULC low-expression plasmid group; HULC-siRNA-NC: HULC low-expression control plasmid group.
- Citation: Cao SQ, Zheng H, Sun BC, Wang ZL, Liu T, Guo DH, Shen ZY. Long non-coding RNA highly up-regulated in liver cancer promotes exosome secretion. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(35): 5283-5299
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i35/5283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i35.5283