Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2019; 25(34): 5120-5133
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120
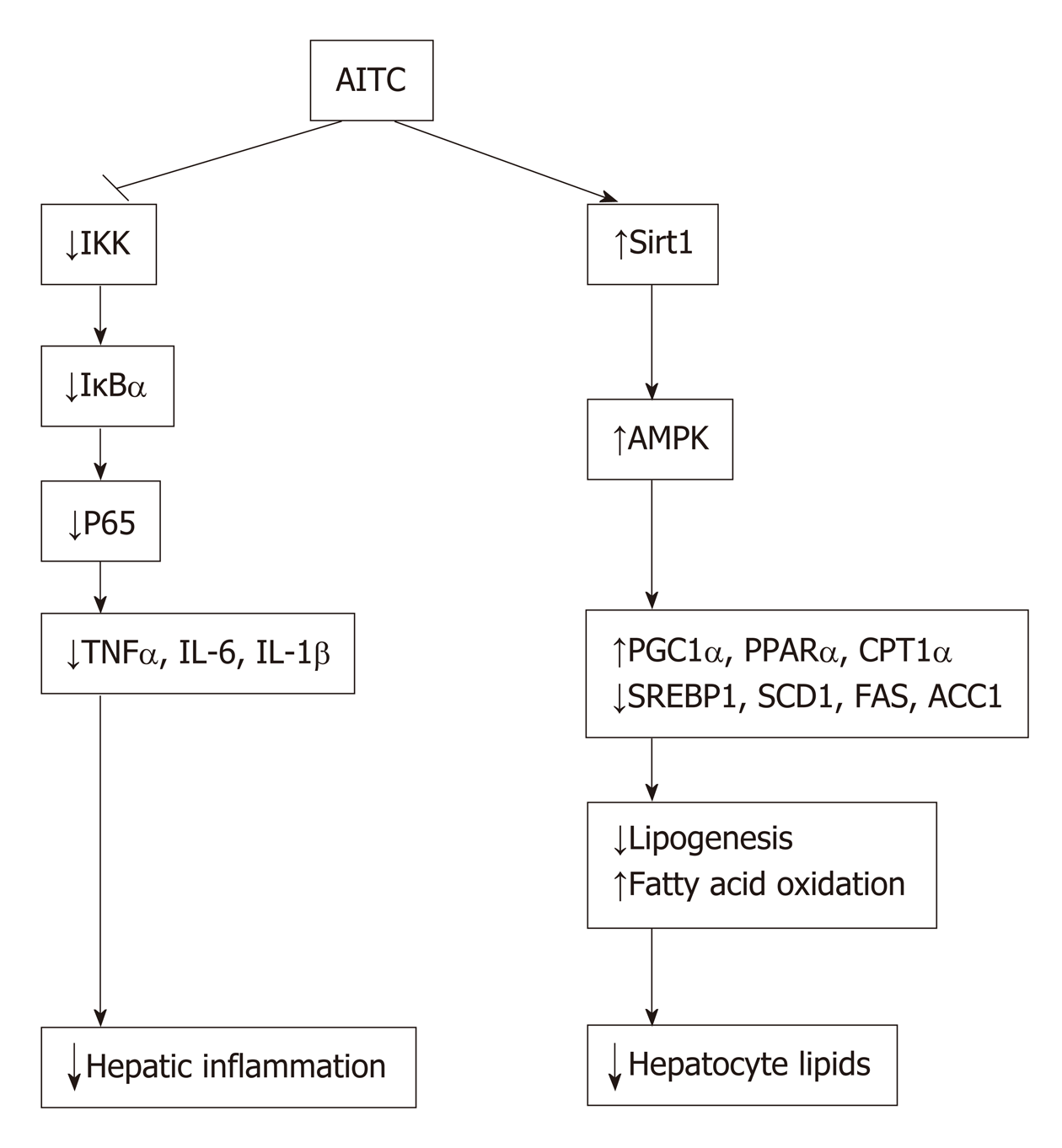
Figure 8 Model of allyl isothiocyanate action.
Schematic diagram: allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and hepatic inflammation by activating the Sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; IKK: IκB kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; AMPKα: AMP-activated protein kinase α; PGC1α: Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; CPT1α: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 α; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1.
- Citation: Li CX, Gao JG, Wan XY, Chen Y, Xu CF, Feng ZM, Zeng H, Lin YM, Ma H, Xu P, Yu CH, Li YM. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the Sirt1/AMPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(34): 5120-5133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i34/5120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120