Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2019; 25(34): 5120-5133
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120
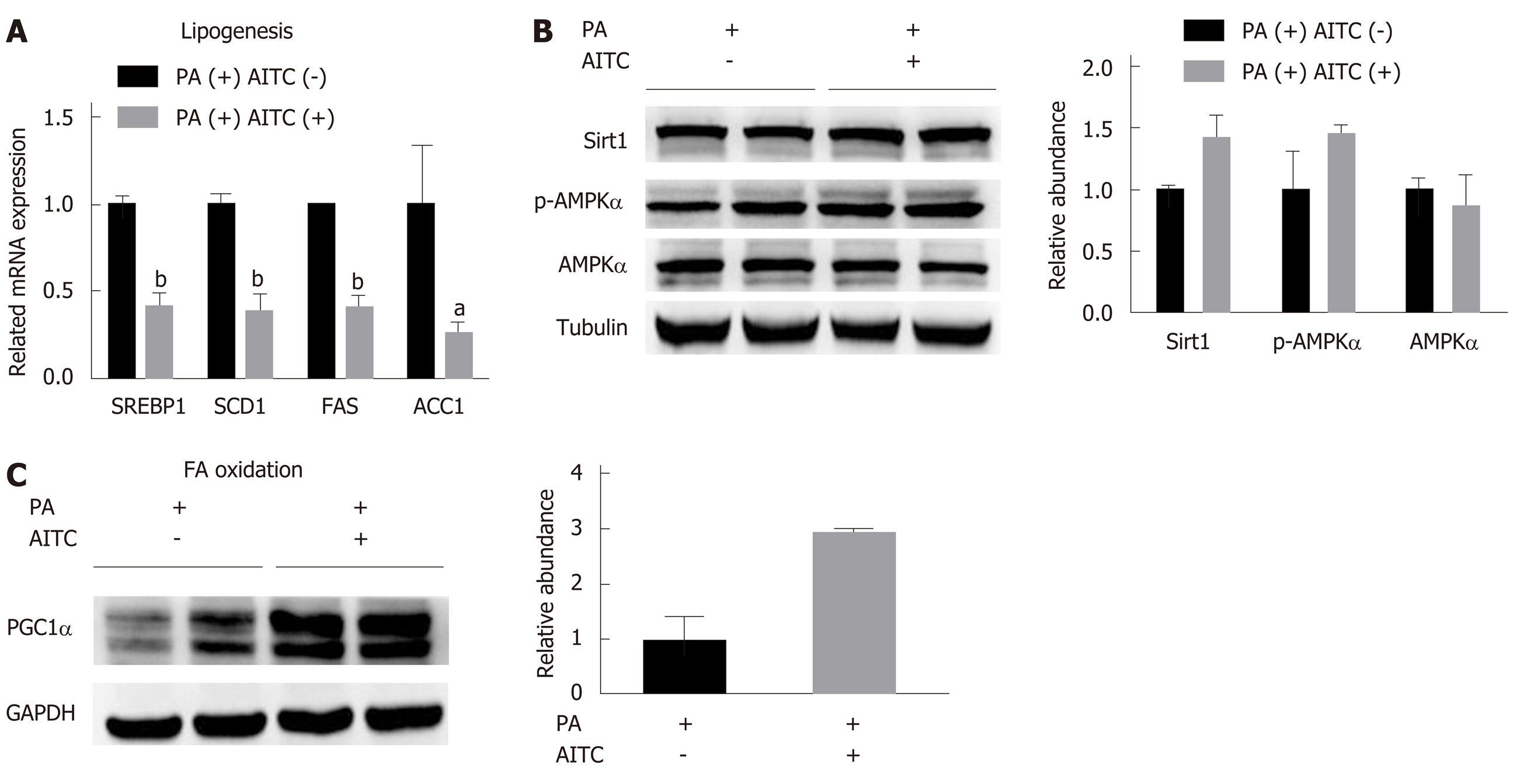
Figure 5 Allyl isothiocyanate downregulates the mRNA levels of genes involved in lipogenesis, upregulates the mRNA levels of genes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation and activates the Sirtuin 1/AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in vitro.
A: Palmitate acid (PA) (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) (20 μmol/L) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle) for 6 h (n = 3/group). The mRNA levels of sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1 (SREBP1) and its lipogenesis target genes, including stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1), fatty acid synthase (FAS) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), were determined. B: PA (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with AITC (20 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle) for 24 h. The protein expression of Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1), total and phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) was detected by western blot analysis. C: PA (200 μmol/L)-stimulated AML-12 cells were treated with AITC (20 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle) for 24 h. The protein level of proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator1α (PGC1α), which is involved in fatty acid β-oxidation, was detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs PA(+) AITC(-). PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; PGC1α: Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; AMPKα: AMP-activated protein kinase α; p-AMPKα: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α.
- Citation: Li CX, Gao JG, Wan XY, Chen Y, Xu CF, Feng ZM, Zeng H, Lin YM, Ma H, Xu P, Yu CH, Li YM. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the Sirt1/AMPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(34): 5120-5133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i34/5120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120