Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2019; 25(34): 5026-5048
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5026
Published online Sep 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5026
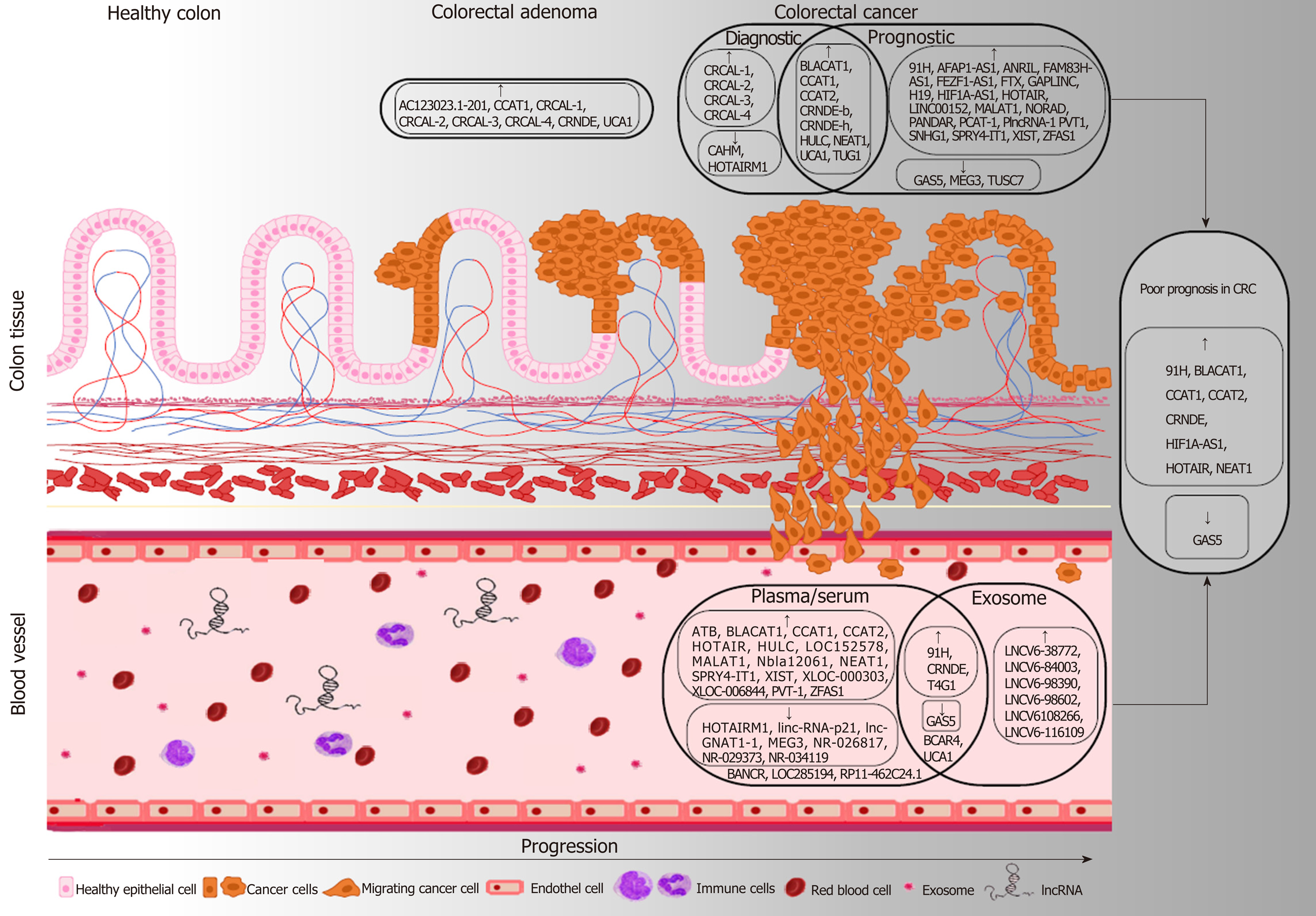
Figure 1 The most important tissue and circulating long non-coding RNA candidates with diagnostic and prognostic potential in colorectal tumors.
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs) upregulated in adenoma or colorectal cancer (CRC) samples compared to normal controls are marked with ↑, while the downregulated lncRNAs are depicted with ↓. Potential prognostic markers detectable both in tissue and blood specimens are highlighted in the right, where ↑ refers to lncRNAs whose higher levels were found to be associated with poor prognosis (CRNDE, HOTAIR, CCAT2, BLACAT1, CCAT1, NEAT1, 91H, HIF1A-AS1), while the low expression of lncRNA marked with ↓(GAS5) can be a predictor of worse disease outcome in CRC patients. In case of the lncRNAs written without frame (BANCR, BCAR4, LOC285194, RP11-462C24.1, UCA1), diverse, sometimes controversial expression data are available in the scientific literature.
- Citation: Galamb O, Barták BK, Kalmár A, Nagy ZB, Szigeti KA, Tulassay Z, Igaz P, Molnár B. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of tissue and circulating long non-coding RNAs in colorectal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(34): 5026-5048
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i34/5026.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5026