Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2019; 25(33): 4904-4920
Published online Sep 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4904
Published online Sep 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4904
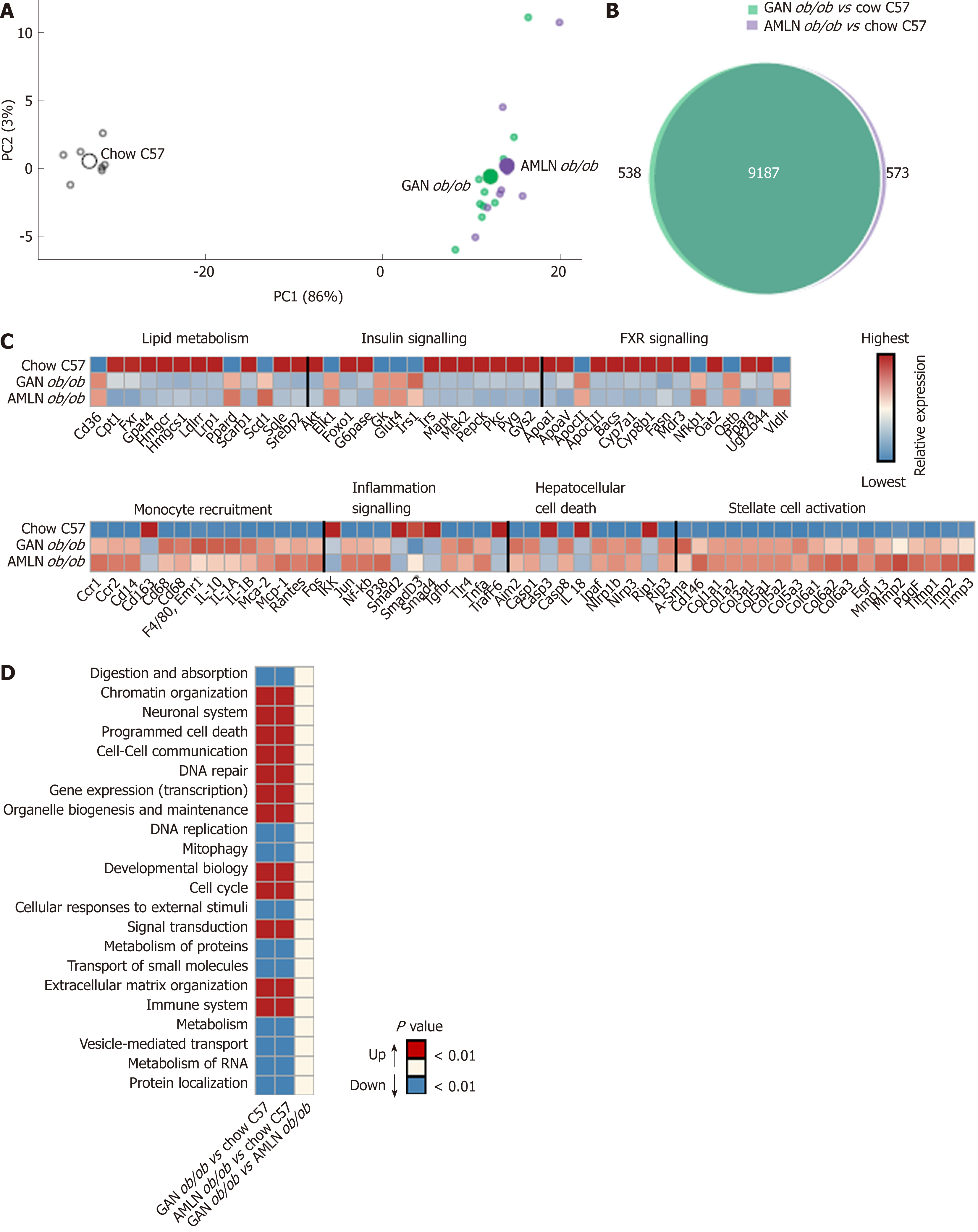
Figure 4 Liver transcriptome changes in ob/ob mice fed amylin liver non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (AMLN) or Gubra amylin non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (GAN) diet for 16 wk.
Overview of hepatic gene expression profiles in ob/ob mice fed amylin liver non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (AMLN) or Gubra amylin non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (GAN) diet compared to age-matched chow-fed ob/ob mice (n = 8-10 mice per group). A: Principal component analysis of samples based on top 500 most variable gene expression levels; B: Group-wise comparison of total number of differentially expressed genes (false discovery rate < 0.05) between ob/ob mice fed AMLN or GAN diet for 16 wk vs chow-fed C57BL/6J (Chow C57) mice; C: Relative gene expression levels (z-scores) of differentially regulated candidate genes associated with NASH and fibrosis. In-house gene panel on candidate genes is indicated in Supplemental Table 1; D: Group-wise comparison of global liver transcriptome changes according to enrichment of individual gene sets in the Reactome pathway database. Regulated pathways are ranked according to level of statistical significance (P value). AMLN: Amylin liver non-alcoholic steatohepatitis diet; GAN: Gubra amylin non-alcoholic steatohepatitis diet; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Boland ML, Oró D, Tølbøl KS, Thrane ST, Nielsen JC, Cohen TS, Tabor DE, Fernandes F, Tovchigrechko A, Veidal SS, Warrener P, Sellman BR, Jelsing J, Feigh M, Vrang N, Trevaskis JL, Hansen HH. Towards a standard diet-induced and biopsy-confirmed mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Impact of dietary fat source. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(33): 4904-4920
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i33/4904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4904