Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2019; 25(32): 4614-4628
Published online Aug 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4614
Published online Aug 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4614
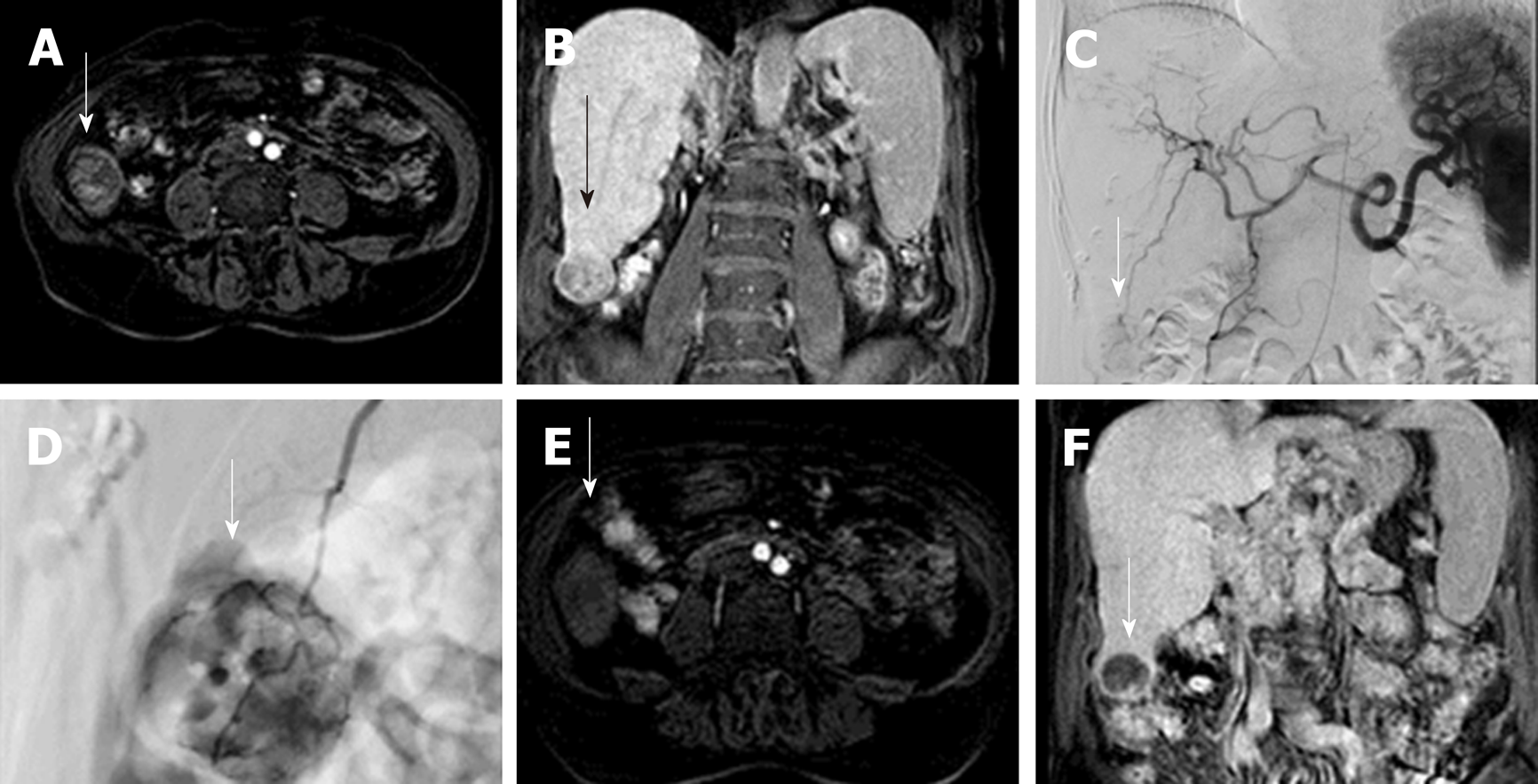
Figure 1 Drug Eluting Beads-Trans Arterial Chemo Embolization of 3 cm hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Gd-EOB- DTPA enhanced MR image of a 73 years old cirrhotic patient with a 3-cm exophytic liver nodule in segment VI (arrow), showing enhancement in the arterial phase; B: the nodule is hypointense in comparison to the surrounding liver parenchyma in coronal hepatobiliary phase, in keeping with HCC. C and D: Celiac axis DSA showing the hypervascular lesion (arrow); selective microcatheterization of the feeding vessel with infusion of doxorubicin-loaded drug-eluting beads (200 µm). E and F: 2-mo follow-up Gd-EOB- DTPA enhanced MR image demonstrating absence of arterial enhancement of the nodule and marked hypointensity in coronal hepatobiliary phase (arrow).
- Citation: Inchingolo R, Posa A, Mariappan M, Spiliopoulos S. Locoregional treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current evidence and future directions. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(32): 4614-4628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i32/4614.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4614