Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2019; 25(31): 4468-4480
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4468
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4468
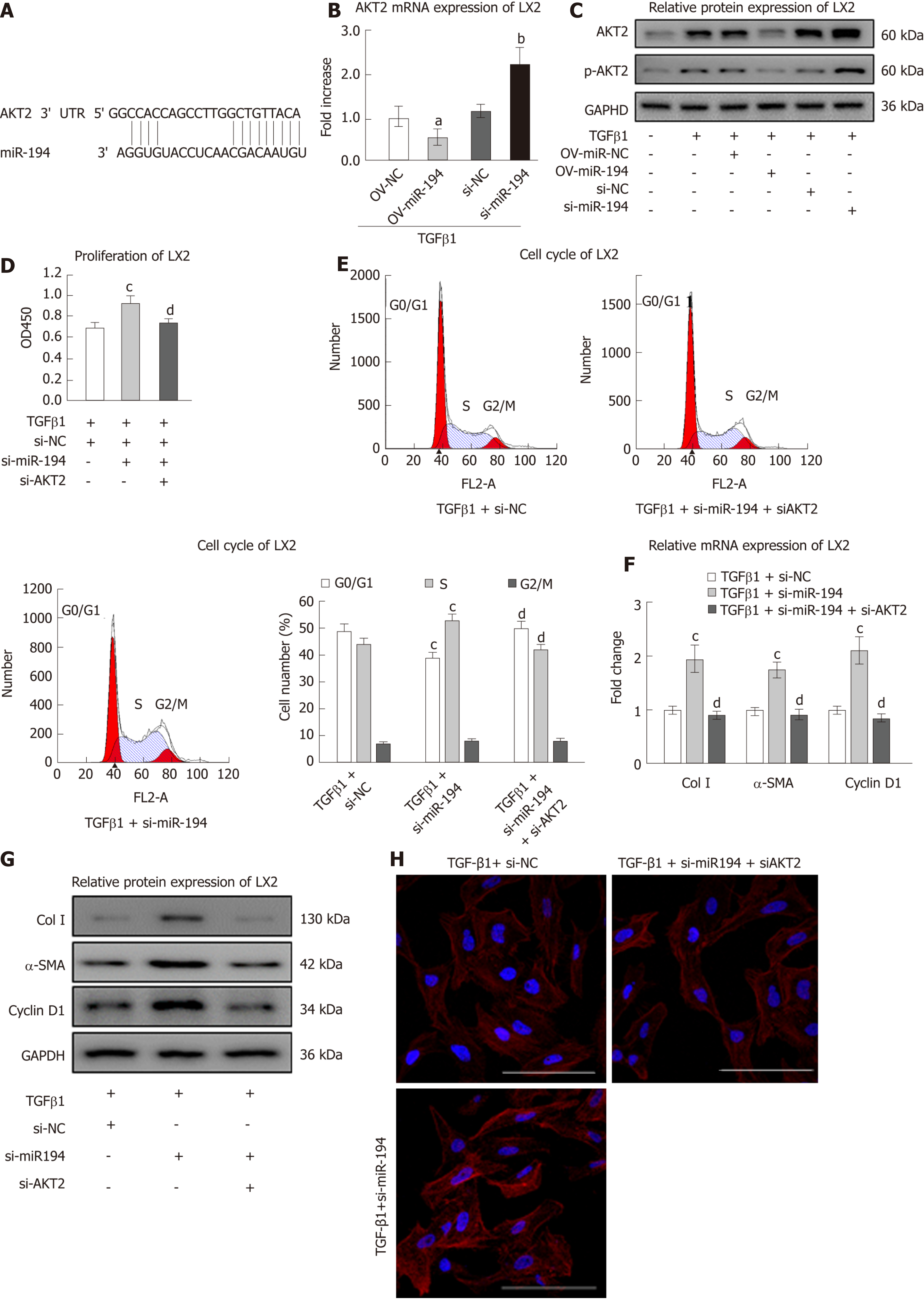
Figure 4 iR-194 performs multiple functions by inhibiting AKT2 in hepatic stellate cells.
A: Binding sites of miR-194 to AKT2 predicted with TargetScan software; B: LX2 cells were treated with OV-miR-194/si-miR-194±TGF-β1. The expression of AKT2 mRNA was measured by qPCR; C: The AKT2/p-AKT2 protein levels measured by Western blot; D: LX2 cells were then transfected with si-miR-194 or si-AKT2. The CCK8 assay showed the proliferation of LX2 cells; E: The cell cycle analyzed by flow cytometry; F: The mRNA expression of Col I, α-SMA, and cyclin D1 measured by qPCR; G: The protein expression of Col I, α-SMA, and cyclin D1 measured by Western blot; H: IF was used to analyze the α-SMA protein levels in LX2 cells. Bar = 100 μm. aP < 0.05 vs the TGF-β1 + OV-miR-NC; bP < 0.05 vs the TGF-β1 + si-NC group group, cP < 0.05 vs the TGF-β1 + si-NC group; dP < 0.05 vs the TGF-β1 + si-miR-194 group. α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; Col I: Type I collagen.
- Citation: Wu JC, Chen R, Luo X, Li ZH, Luo SZ, Xu MY. MicroRNA-194 inactivates hepatic stellate cells and alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting AKT2. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(31): 4468-4480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i31/4468.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4468